Classification
Domain Eukarya:This
domain is characterized by the possession of a true nucleus and
membrane-bound organelles.
Kingdom Animalia:All
animals are multicellular organisms made up of eukaryotic cells.
They are heterotrophic and acquire their nutrients via
ingestion.
Phylum Arthropoda: Arthropods
are the largest and most diverse animal phylum. They are
distinguished by their segmented bodies and their complex
jointed exoskeletons. Most members of this phylum also have
distinct body regions.
Subphylum Crustacea: Crustaceans
are primarily aquatic and have two distinct regions, a
cephalothorax and an abdomen. Most species also have two pairs
of antennae and compound eyes.
Class Branchiopoda: This
class is characterized by the presence of a carapace, swimming
appendages, and a large compound eye. They also all have
mouthparts that are either lacking or reduced in size.
Order Cladocera: Cladocera
are the commonly known group known as the water fleas which
inhibit mostly fresh waters. They are defined by their unique
brood chamber, called the ephippium as well as their means of
reproduction called parthenogenesis.
Family Daphniidae:
Genus Daphnia:
The Genus Daphnia is characterized by its transparent carapace.
Other prominent features are its compound eye, second pair of
antennae, and a pair of abdominal setae.
Species, Daphnia pulex: Although D. pulex is hard to distinguish from a number of closely related forms, it is characterized by its small size, and the fact that one of the appendages near the postabdomen is full of setae. Also, the ephippium is more triangluar than most species, and the embryos are not parallel. In addition, there is only one extension from the top edge of the ephippium, and the body segmention is nearly invisible.

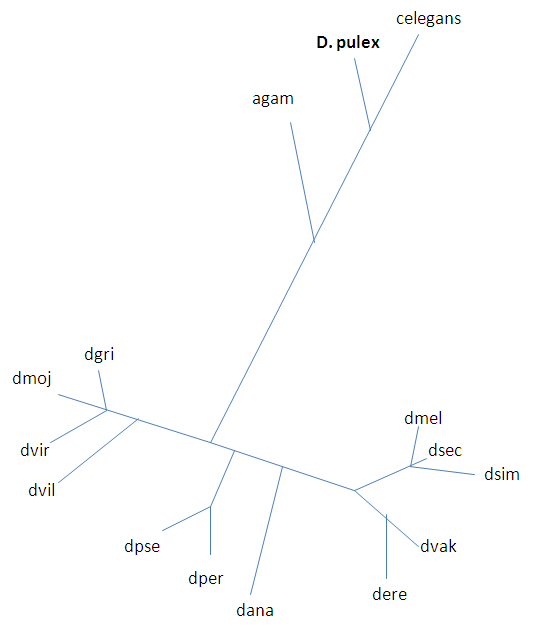
This demonstrates the classification of D. pulex according to genome.
Find out about where the Daphnia lives.
Go back home.