Facts
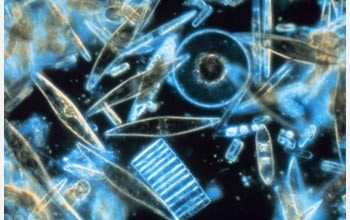
Diatoms are very unique organisms that are very diverse. They
also have the ability to in just abou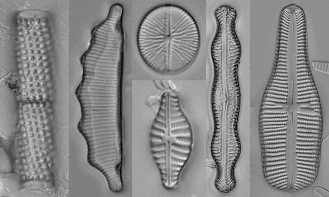 t every ecosystem in some
shape or form. But, further more they have something that no
other organism has, a glass cell wall called a frustule. Its
presence gives the diatoms a large amount of advantages and
causes them to be a large interest to humans because of its
unique beauty and because it is one of the only microorganisms
that will fossilize because of it being hard tissue. The
frustule is also rather complex and deals with a large amount of
what the diatom is able to do.
t every ecosystem in some
shape or form. But, further more they have something that no
other organism has, a glass cell wall called a frustule. Its
presence gives the diatoms a large amount of advantages and
causes them to be a large interest to humans because of its
unique beauty and because it is one of the only microorganisms
that will fossilize because of it being hard tissue. The
frustule is also rather complex and deals with a large amount of
what the diatom is able to do.
The frustule is made out of silicon. The diatoms obtain the
silicon in the form of silicic acid this is at fairly high
concentrations in waters worldwide, because silicon is one of
the most prevalent elements on earth and gets consciously washed
into the oceans via rivers and rain runoff. The frustule is
composed of two parts or valves. They are uneven in size and fit
together like a Petri dish or a pill box. The larger part is
called the epitheca and the smaller part is the hypotheca. They
are produced at two parts in the diatoms life cycle. The most
common form is when the diatom is
reproducing asexually each of the divided cells will take
one of the valves as the epitheca and will secrete the hypotheca,
this causes one of the diatoms involved in the division to
gradually get smaller and smaller. The other part in which the
cell produces the frustule during sexual reproduction and it is
formed with in the auxospore. Within the auxospore both valves
are produced they are produced at the maximum size that the
frustule for that diatom species can be to compensate for the
gradual reduction in size caused by asexual reproduction.
The function of the frustule is rather diverse and can vary to a
degree d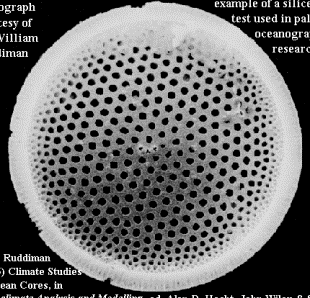 epending on species and habitat.
The primary functions of the frustule though that is shared
though species is rather fundamental. The functions include, but
are not restricted to, providing support, protection from
predation, attachment to surfaces and substrates, change the
buoyancy of the organism (placement in water column), in
terrestrial habitats it allows organisms to help maintain water,
and it helps refract and reflect light on the inside of the
organism causing a greater amount of light contact to the
photosystems and increasing the effectiveness of cell to fix
carbon. The frustule proves a lot more functions although not
all of these apply to all species of diatom, such as organism
that attach to surfaces of substrates don’t have frustules that
affect the organisms buoyancy. The different attributes of the
frustule are attributed to various features that are present on
the diatoms.
epending on species and habitat.
The primary functions of the frustule though that is shared
though species is rather fundamental. The functions include, but
are not restricted to, providing support, protection from
predation, attachment to surfaces and substrates, change the
buoyancy of the organism (placement in water column), in
terrestrial habitats it allows organisms to help maintain water,
and it helps refract and reflect light on the inside of the
organism causing a greater amount of light contact to the
photosystems and increasing the effectiveness of cell to fix
carbon. The frustule proves a lot more functions although not
all of these apply to all species of diatom, such as organism
that attach to surfaces of substrates don’t have frustules that
affect the organisms buoyancy. The different attributes of the
frustule are attributed to various features that are present on
the diatoms.
The features that are present on the frustules of diatoms are
various and include different combinations, sizes and
ordinations of pores, spines and some other features. The spines
are used in variou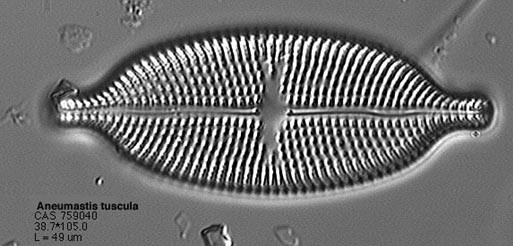 s means such as providing some protection
from predation and the ability to attach to various substrates.
The pores allow transport of various solutions in and out, as
well as, slimes out of the cell. The pores
allow the diatom to obtain some nutrients from the different
sources as well as to allow them to secrete some the their
extracellular polysaccharides. Some species of diatoms can also use the pores to
assist in the locomotion via gliding. There are other structures
the diatoms use that are on the frustule that do other
structures.
s means such as providing some protection
from predation and the ability to attach to various substrates.
The pores allow transport of various solutions in and out, as
well as, slimes out of the cell. The pores
allow the diatom to obtain some nutrients from the different
sources as well as to allow them to secrete some the their
extracellular polysaccharides. Some species of diatoms can also use the pores to
assist in the locomotion via gliding. There are other structures
the diatoms use that are on the frustule that do other
structures.
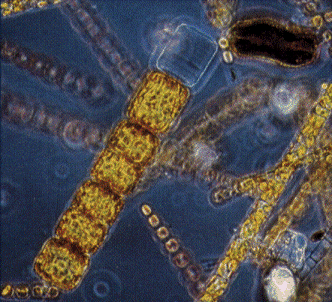
Beyond the structure and use of the frustules diatoms other
promising features that can be put to use because the majority
of them are grow in open ocean and because of that it limits the
growth because the lack of iron. Although, because diatoms
acquisition carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, plans have been
brought together to fertilize open ocean areas with iron that
will facilitate diatoms in the area to grow. This causing them
to talk up carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and this could
reduce the carbon omissions and combat global warming.
To References
For other sites of diatoms go to http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/chromista/bacillariophyta.html, or http://www.indiana.edu/~diatom/diatom.html.