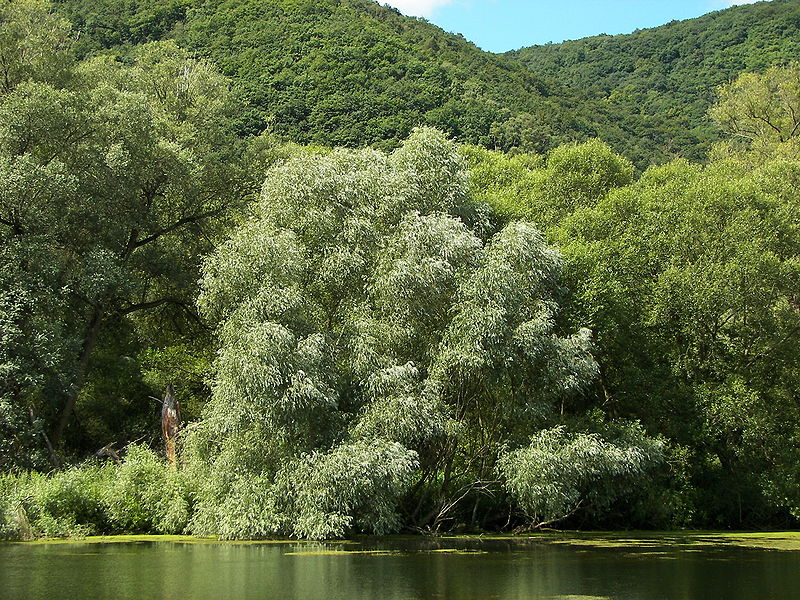
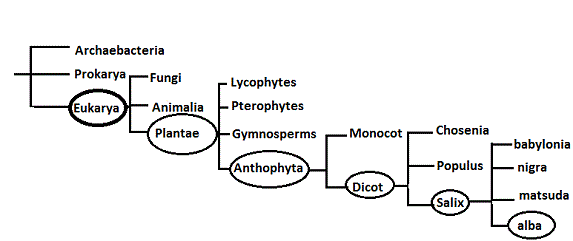
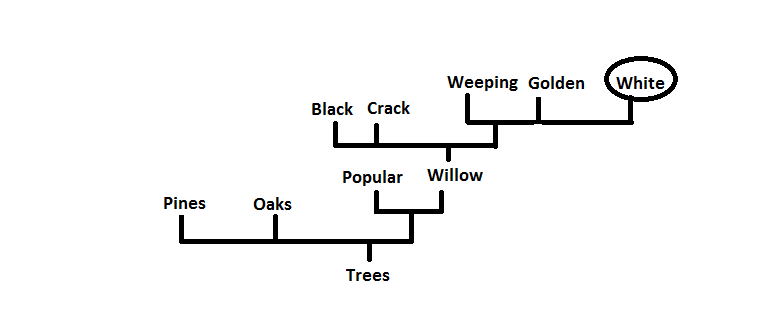
Where does Salix alba fit in with all the other organisms?
Kingdom:
Willows are under the kingdom Plantae because the cell walls are made of cellulose that support the tree. Also, inside the leaves are chloroplasts, which also put in under the plantae kingdom. As a side note, willows are in the subkingdom of vascular plants. This is because they contain xylem and phloem used to transport water and nutrients through out the trees.
Phylum:
Willows are under the Anthophyta phylum because they contain covered seeds. Specifically, the seeds in a white willow reside in flowers clumped together in what is called a catkin. The common referral to plants with covered seeds is called angiosperms. This is also a correct reference to the white willow. All sorts of plants fit under this category from the sweet orange to a hibiscus.
Class:
The white willow is in the class Dicotyledonae. Also known as dicot plants, white willows fit under this group because their flowers i.e. catkins have two embryonic leaves. Another way to distinguish white willows into this group is that the flower has four or five parts. This additionally puts it in the dicotyledonae class.
Order:
The order of the white willow is Salicales. The willows fit into this group because they are dioecious, woody plants, with alternate, simple, stipulate leaves and much reduced flowers that are grouped into catkins.
This is a phylogenetic tree based on the morphology of species. Created by Steven Girard.
Family:
The white willow is in the family Salicaceae. White willow fits into this group because the tree's staminate flower contains two stamens. Also, because the imperfect flowers are produced in catkins and are dioecious. Here is a good website with more information about the salicaceae family montara.com.
Genus:
The genus of the white willow is Salix. This is the genus of the commonly known willow trees of multiple species. One of the characteristics that put the white willow in this group is that the sap contains a heavy concentration of salicylic acid.
Species:
This is what makes the white willow a definable single entity. The species is called Salix alba. In English alba translates to white, and Salix is willow. Literally meaning Willow white.
Salix alba hybridizes easily due to the fact different willow species can cross pollinate each other. This makes distinguishing Salix alba from other species very difficult. Some of the things that separates Salix alba are the male catkins are yellow and fatter than typical catkins and the level of salicylic acid tends to be greater. This along with the classic white leaves with the threads on bottom allow for identification of this specific species.
Below you will find phylogenetic trees based on certain attributes. After looking at those we will look into the habitat of Salix alba
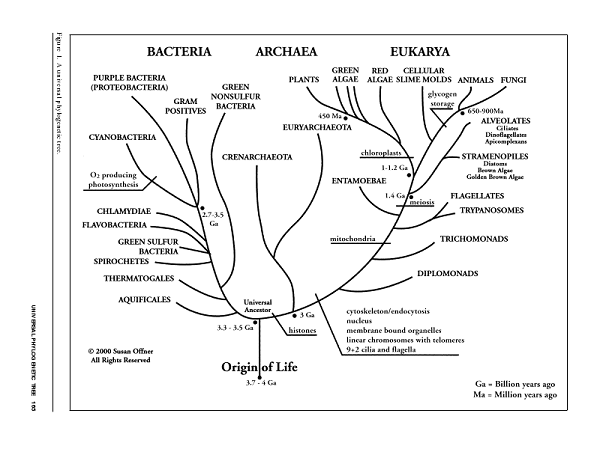
Here is a different phylogenetic tree created by Susan Offner based on genome sequencing. This chart provides a wider view of where willows are in the grand scheme of all organisms. The white willow is under the plants section.