Want to know more about these
fascinating snakes?
Here's some
more facts
- The Bamboo pit viper's fangs are a hollow tube hooked up to
venom producing sacks behind the
 snakes eyes. Bamboo pit viper fangs are so long that they fold up to the roof of the viper's mouth so they wont bite themselves.
snakes eyes. Bamboo pit viper fangs are so long that they fold up to the roof of the viper's mouth so they wont bite themselves.
- If a snake loses a fang, it will simply grow another one.
- Bamboo pit vipers hunt mostly at night by using heat sensing
pit organs.
- Ever wonder how a snake can
breath when their mouth is full of
prey? Snakes have small tubes
in the back of their throat that
stick out far enough to draw air in so they won't pass
out while trying to swallow.
- A snakes throat takes up to a third of its body.
- Why do snakes not blink? Because they don't have eyelids!
Instead, snake eyes are covered with a clear scale called a
spectacle.
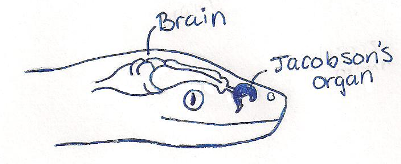
- How does a pit viper smell? Not with its nose! Instead, a snake sticks out its tongue to collect scents. When the tongue is drawn back in the mouth it touches the Jacobson's organ on the roof of the mouth, which tells the pit viper what it is smelling.
-
Did you know all snakes, including the Bamboo pit viper are deaf. While they cannot hear, snakes can sense vibrations with the Jacobson's organ to give them a sense of what's around them.
-
Ophidiophobia is the fear of snakes.
Want to read more about snakes? Here's some great websites on snakes by my fellow Organismal Biology classmates. Check them out see how much variety there is among snakes.
-
The timber rattlesnake Crotalus horridus. Like the Bamboo pit viper, this snake is a member of the pit vipers and they are both in the Viperidae family. This snake and the Bamboo pit viper are pretty similar-both having pit organs and hemotoxic venom- but each have adopted to their different niche.
-
The northern banded water snake Nerodia sipedon. Both the Bamboo pit viper and this snake are in the Squamata order, but this snake lacks the pit organs and is not venomous.
-
The eastern massasauga Rattlesnake Sistrurus catenatus. This snake is also a member of the pit vipers and is found in dry regions North America, as opposed to the wet regions of India the Bamboo pit viper resides in.
-
The cottonmouth snake Agkistrodon piscivorus. The cottonmouth is yet another member of the pit vipers. This snakes lives in the southern United States, and much of its diet is the same as the Bamboo pit viper's diet in India.
-
The reticulated python Python reticulatus. Though the Bamboo pit viper and the python both in the order Squamata, these two snakes are very different. The Python does not use venom to capture its prey, instead the python squeezes its prey to death. This snake also hunts much larger prey and can therefore grow much larger then the Bamboo pit viper.
-
The Inland Taipan snake Oxyuranus Microlepidotus. Like the Bamboo pit viper, this is a venomous snake, However, this snake has earned the nickname 'fierce snake' because it is the most venomous land snake known. This snake lives in the rough Australian outback, and if you ever see it run the other way!
Continue to my
references
Go back home