Glossary

Adhesion: two unlike materials being held together
by attraction and force; an example would be between water and the xylem
cells of a plant as the water is forced through the transport system;
can easily be confused with cohesion (look to the right for an example
of adhesion and cohesion)
Alzheimer’s disease: a common form of dementia that
consists of the degeneration of the brain; some symptoms include memory
loss, confusion, disorientation, changes in mood, behavior, and
personality, and lack of initiative; most common in elderly population
Antioxidants: a substance that has the ability to
donate an electron of its own (without becoming unstable) to stabilize a
free radical
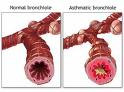
Asthma: a respiratory disease that causes wheezing,
coughing, shortness of breath, and other such symptoms
(picture to the left)
Arteries: blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood to
the tissues or capillaries
Arteriosclerosis: a disease that is most commonly found
in the elderly and it causes the arteries to harden
Atherosclerosis: a disease where low density
lipoprotein cholesterol and fatty acids build up and cause unwanted
clogged blood vessels
ATP: (Adenine triphosphate) a molecule that specializes
in energy storage
Capillaries: blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood
to the smaller parts of the body where the arteries cannot reach
Calvin Cycle: a cycle in photosynthesis that is
responsible for converting the ATP, NADPH and carbon dioxide into
glucose by going through a series of revolutions
Cohesion: two materials that are similar being held
together by attraction or force; an example would be how water can stick
to itself as it is being forced through the transport system; can easily
be confused with adhesion (see Adhesion for a picture)
 Dichotomous veins: veins on a leaf that continuously
branch into two equal parts (picture to the left)
Dichotomous veins: veins on a leaf that continuously
branch into two equal parts (picture to the left)
Dioecious: (two houses) describes an
organism that is either male or female; does not have both reproductive
organs in the same organism
Deciduous: describes an organism that drops its leaves
(or needles) annually
Dementia: a disease most common in older people that
occurs because of damage to the neurons in the brain, causing sever
degeneration and impairment
Electron: a negatively charged particle in an atom,
located in orbitals rotating around the nucleus
Endotrophic mycorrhizae: a specific type of fungi that
can be found on the roots of many plants (specifically the Ginkgo biloba)
and that aid in supplying the plant with nutrients such as phosphorus
and nitrogen
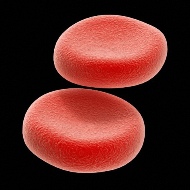
Erythrocytes: commonly known as red blood cells; these
cells function to carry oxygen to the cells of the body (look right for
a picture of two erythrocytes)
Evaporation: when a material changes states from liquid
to gas; this can happen in plants when the water on the leaves get
changed into water vapor from the sun’s heat
Free Radicals: A molecule that has lost and electron
and has become unstable because of it; a free radical will then try to
replace its lost electron with one from tissues around it and a vicious
cycle occurs
Fan-shaped leaves: leaves in the shape of a rounded
triangle, similar to the paper fans some people use to cool themselves
Flagellated Sperm Cells: a specific type of motile
sperm that has an extremely slender, whip-like motion used to move the
body of the cell; the flagella kind of looks like a string, but does not
have the same function
Flavone glycosides (flavonoids): a specific part of
Ginkgo biloba extract that that holds the key to many of the
medicinal purposes; specifically these components are antioxidants

Fruit: some people refer to the covering on the seed of
Ginkgo biloba as a fruit, but the Ginkgo biloba doesn’t have a
fruit; it is just an outer casing on the “naked” seed that can resemble
a fruit-like body (look to the right for a picture)
Fungal hyphae: a system of thread-like fibers used for
fungal growth; they have a cell wall typically made of chitin
Glaucoma: a disease that causes blindness due to damage
to the optic nerve
Glomeromycota fungus: a specific phylum of fungi that
usually forms a mutualistic symbioses with plants (typically on the
roots)
Glucose: a carbon compound that almost all organisms
use for nutrition
GEM study: (Ginkgo Evaluation of Memory) a specific
study led by Stephan T. DeKosky in which the effects of Ginkgo biloba on
Alzheimer’s disease were recorded.
Hepatitis B: a disease that is passed by contaminated
blood or other fluids of the body and has serious effects on the liver
 Jurassic period: a time period from about 190 million
years ago to 135 million years ago when some dinosaurs roamed the Earth
(look to the left for a scary surprise!)
Jurassic period: a time period from about 190 million
years ago to 135 million years ago when some dinosaurs roamed the Earth
(look to the left for a scary surprise!)
Impotence: the inability for a male to maintain an
erection during sexual intercourse
Leukocytes: commonly known as white blood cells, these
cells function to fight off infections from foreign invaders
Low density lipoprotein: the ‘bad’ type of cholesterol that contains a lot
of lipids and proteins
Macular Degeneration: vision loss due to retina
degeneration
Motile Sperm: sperm cells that can move; in the case of
Ginkgo biloba, the sperm cells have flagellated sperm
Mutualistic symbioses: interactions of two or more
organisms where both (all) species benefit from the other(s); an example
could be the bacteria living inside your stomach; it helps you digest
food and you give it nutrients from the food you eat
NADPH: (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate) a
very complex molecule that carries electrons in photosynthesis
Optic nerve: nerve that runs from the back of the eye
to the brain

Phloem: a hollow “tube” of cells located in vascular
plants that functions in transporting nutrients down the plant (look to
the right for a picture that helps show where the phloem is located in a
plant stem)
Photosynthesis: the process of making nutrients from
sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide
Placebo: a sugar pill (that looks exactly the same as
the other pill in an experiment) that is given to half the participants
in an experiment; the placebo group is important because it is
considered the control group and serves to show what would happen if no
medication was given
Plasma: the liquid part of the blood
Platelets: the component of blood that causes it to
clot
Platelet-activating factors: (PAF) cause clotting in
the blood
 Sessile: unmoving; rooted to a specific spot; immotile
(the Ginkgo tree on the left helps to show how all plants are
sessile)
Sessile: unmoving; rooted to a specific spot; immotile
(the Ginkgo tree on the left helps to show how all plants are
sessile)
Strap-shaped leaves: thin, elongated leaves protruding
from the plant
Terpene lactones (terpenoids): a hydrocarbon that can
be found in Ginkgo biloba; this specific structure is mainly
used for unclogging unwanted blood clots
Tinnitus: a disease that has the sensation of
continuous ringing in one’s ears
Triassic period: a time period from about 230 million
years ago to 190 million years ago
Tuberculosis: an infectious disease that usually occurs
in the lungs
XX/XY chromosomes: chromosomes that determine the sex of an organism;
females have XX chromosomes, males have XY chromosomes
Xylem: a “tube” located in a vascular plant that is in
charge of transporting water
Veins: blood vessels that carry oxygen-poor blood back
to the lungs and heart
Want to not only gain a bigger vocabulary, but also a bigger fact base
about the Ginkgo tree? Visit FABULOUS FACTS
for more information.
HOME
