Nutrition
Piptoporus betulinus is classified as saprobic and parasitic fungus. Unlike plants who can photosynthesize, fungi utilize many hyphae to concur a large surface area to acquire their nutrition. This means the mycelium of the fungus which is an accumulation of many hyphae, feeds off the dying or dead birch tree by producing exoenzymes which break down the substrate or wood. The exoenzymes essentially digest the cellulose of the wood. Then the hyphae grow into the particles and ingest the nutrients as they move.
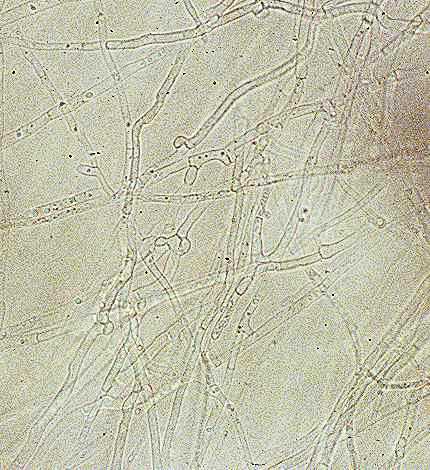 Fungal
Hyphae Photo by Tom Volk
Fungal
Hyphae Photo by Tom Volk
Back to Identification
How does Piptoporus betulinus reproduce? Find out here Reproduction