Habitat
Range:
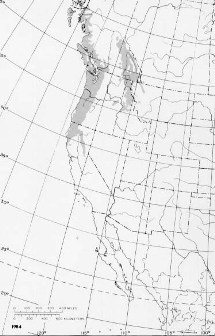
The Pacific Yew grows in a strip from the southern tip
of southeast Alaska all the way down into parts of
California. In Alaska, the tree is found along the
Pacific Coast including places such as Annette and
Prince of Whales Island. From there, the tree moves into
the Rocky Mountain regions of British Columbia in the
southeast to the northwestern parts of Montana and
northern parts of Idaho. Next, it migrates down into
eastern Washington and Oregon. Finally, it moves down
the Pacific Coast of northern California.
Climate:
Taxus brevifolia is found in a wide range of moisture
and temperature conditions. In areas where it’s very dry
or subhumid, the tree is limited to places near streams,
places with shade and the lower third of north-facing
slopes. In areas of the tree’s range that are within
humid and superhumid forests, this tree is typically
found on all slopes, benches and ridgetops.
Soil and Topography:
Soil that is best for Taxus brevifolia is deep, moist or
rich, rocky or gravelly. Some soils that the Pacific Yew
grows well in include those in the order Ultisols,
Alfisols and Inceptisols.
Associated Forest Cover:
The majority of the time, the Pacific Yew is found in
dense old-growth conifer forests where they are able to
inhabit the understory. In these areas, trees such as
Douglas fir, ponderosa pine,
giant redwood and hemlock are also found. In areas
where the trees in the canopy have been removed, the
Pacific Yew is able to flourish.
Take a look at the Adaptations page to see how the Pacific Yew has adapted to its environment!