It's Not Your Normal Relationship...
Red Knot, horseshoe crab
eggs, and close up of horseshoe crab.
Horseshoe crabs are classified under secondary consumers. They consume organisms such as bivalves, worms, and multiple kinds of clams. The pumpkinseed sunfish tend to feed on a lot of mollusks as well! To learn more about the pumpkinseed sunfish click here!
 Horseshoe crabs are important prey for
multiple organisms. Over 11 different
species of shorebirds, especially the red
knot, eat horseshoe crab
eggs as their main food source when
migrating. The eggs
that are found are nests that had been
destroyed by waves or storms. These birds
do not affect the horseshoe crab after it is
out of the egg and growing.
Horseshoe crabs are important prey for
multiple organisms. Over 11 different
species of shorebirds, especially the red
knot, eat horseshoe crab
eggs as their main food source when
migrating. The eggs
that are found are nests that had been
destroyed by waves or storms. These birds
do not affect the horseshoe crab after it is
out of the egg and growing.
Shorebirds are not the only organisms
that feed off of horseshoe crab’s eggs. Many
species of fish such as striped bass, white
perch, killifish, kingfish, silversides, all
crabs, many gastropods, other invertebrates,
fish, sharks, and sea turtles prey on the
eggs and larvae.

Above: shorebirds feeding
on the horseshoe crab's eggs.
Photo by Sheila Eyler, USFWS
Right: Loggerhead Sea Turtle
The older the horseshoe crabs get, the
slower they grow and the less they molt.
At this point in their life it becomes
easier to spot relationships between them
and smaller organisms. The horseshoe
crab forms multiple relationships with small
organisms. Majority of their interactions
with other organisms are commensalism.
Sponges, bivalves, and many snails are often
found just living on their backs and
undersides. Want to learn more about
some cool sponges? Click
here for the sea sponge and click
here for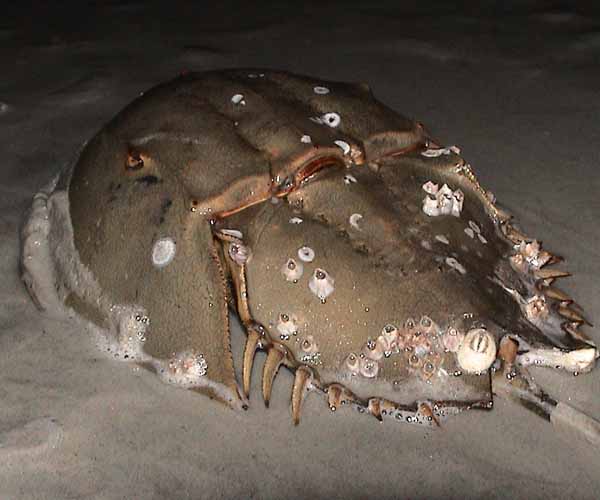 the marine sponge! Periwinkles,
basket, and mud snails lay their eggs on
their backs. However, there are
organisms that are considered parasitic.
The limulus leeches lay their eggs around
the book gills and leg joints of the crabs.
Old female crabs are generally the main target. Often the cuticle of the
gills are utilized as the place for chemical
activity causing harm to the horseshoe crab.
the marine sponge! Periwinkles,
basket, and mud snails lay their eggs on
their backs. However, there are
organisms that are considered parasitic.
The limulus leeches lay their eggs around
the book gills and leg joints of the crabs.
Old female crabs are generally the main target. Often the cuticle of the
gills are utilized as the place for chemical
activity causing harm to the horseshoe crab.
Multiple organisms on a horseshoe crab's back. An example of some of the many symbiotic relationships this organisms exhibits.
Medical Uses
The use of horseshoe crabs in the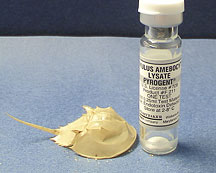 medical
field
often goes under the radar. Not many
people know that we use the horseshoe crab's
blood for many medical purposes including
the safety of drugs and many medical
devices. There is a protein in the
blood called Limulus Amebocyte
Lysate, LAL and it is used to test medical
products for endotoxins. Endotoxins
can cause fevers as well as the death of
humans.
medical
field
often goes under the radar. Not many
people know that we use the horseshoe crab's
blood for many medical purposes including
the safety of drugs and many medical
devices. There is a protein in the
blood called Limulus Amebocyte
Lysate, LAL and it is used to test medical
products for endotoxins. Endotoxins
can cause fevers as well as the death of
humans.
Above: This is a bottle of LAL, the gel that came from
horseshoe crab
blood
Left: This is a photo of harvested
horseshoe crabs being prepared for LAL
production.
Biomedical companies harvest horseshoe crabs to extract a certain amount of its blood. Only a small amount of blood is drawn from the organism so that it can continue to live. To learn more about some of the the research studies on Atlantic horseshoe crabs, go to http://www.ceoe.udel.edu/horseshoecrab/index.html.
If you would like to learn some interesting facts about the horseshoe crab click here!
To go back to the reproduction page click here.
To go back to the home page click here.

