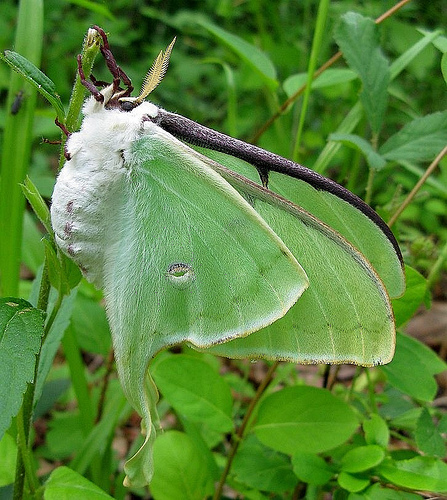
Classification
The complete scientific taxonomic
classification of Actias luna, otherwise known as the luna moth, is as follows:

Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Opisthokonta
Phylum: Arthropoda
Class: Insecta
Order:
Lepidoptera
Superfamily: Bombycoidea
Family: Saturniidae
Subfamily: Saturniinae
Genus: Actias
Species:
Actias luna (Linnaeus 1758)
But what does it all mean??
Actias luna is in the domain Eukarya because its
organelles, or cell parts, are bound and protected by some sort
of membrane. It falls into the kingdom Opisthokonta due to its
possession, at some point in its life, of swimming cells that
have a posterior (opistho) flagella (kont). These "swimming
cells" are most likely male sperm cells. A. luna is
considered an arthropod because it has a segmented body completely covered
with a chitinous exoskeleton, it molts (sheds its exoskeleton) at
least once in its life cycle, and it has jointed (arthro) feet (poda).
Even though they are in the same phylum, the
snow
crab and luna moth have extremely different looking
exoskeletons! Actias luna organism can be classified in the class insecta because
they have a compound eye, two pairs of wings, one pair of
antennae and three body parts: head; thorax; and abdomen. Other
organisms in this class include the
cicada, different types of
flies,
beetles, and
hornets. The luna moth is in the order Lepidoptera because it
is a moth and has wings covered with scales, although these
scales are much different than those we might associate
 with
a
snake or
fish. Bombycoidea
is the superfamily taxon because males of this organism have
much larger bipectinate antennae than females. This difference
can even be seen with the naked eye, and is also very helpful
with
a
snake or
fish. Bombycoidea
is the superfamily taxon because males of this organism have
much larger bipectinate antennae than females. This difference
can even be seen with the naked eye, and is also very helpful
 when trying to distinguish between male and female. The family name Saturniidae is fit for Actias luna
due
to the organism's dorsal eyespots and large
caterpillar characterized with
unique spiney projections. Another moth that falls under this
family is the moth.
The luna moth is in the subfamily Saturniinae because it is
considered to be a giant silkworm moth. The genus Actias
and the species name Actias luna represent this moth's
interesting lifestyle of being mainly active at night,
specifically in the hours immediately following midnight.
when trying to distinguish between male and female. The family name Saturniidae is fit for Actias luna
due
to the organism's dorsal eyespots and large
caterpillar characterized with
unique spiney projections. Another moth that falls under this
family is the moth.
The luna moth is in the subfamily Saturniinae because it is
considered to be a giant silkworm moth. The genus Actias
and the species name Actias luna represent this moth's
interesting lifestyle of being mainly active at night,
specifically in the hours immediately following midnight.
Let's take another approach!
Each of the different characteristics of Actias luna make it an extremely unique organism, but also aide us in classifying where it belongs in relation to organisms and species through taxonomic classification. Another look at how the luna moth is related to other organisms can be seen in a cladistic phylogenetic tree.
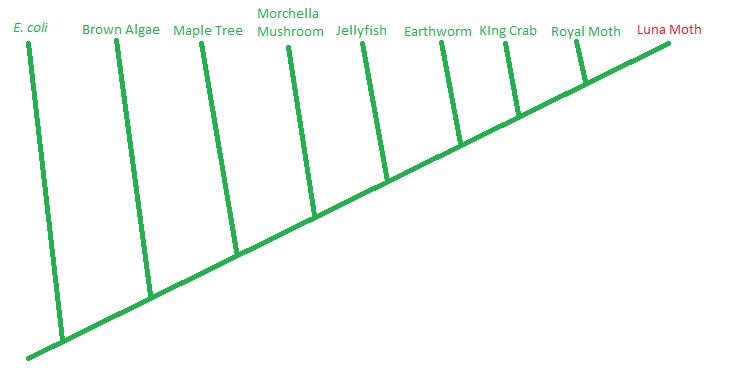
This phylogenetic tree shows the general divergence pattern of the luna moth and where it fits in compared to other organisms on planet earth. This general tree is based off both morphological and molecular data that has been researched and put together by scientists and is widely used in today's science world. Each node on the tree represents the most recent common ancestor of every organism that follows it. When looking at this tree I created, we can see that the royal moth and the luna moth have a more recent common ancestor than the morcella and the luna moth, which means that the royal moth and the luna moth are more closely related. The luna moth and E. coli, a commonly known bacteria, have the most ancient common ancestor, and are therefore the least related according to this technically hypothetical tree.
This next tree just looks at the order Lepidoptera, otherwise known as moth. Every single one of these moths shares a common ancestor, but some share a MORE RECENT common ancestor than others. For example the rosy maple moth and the luna moth are in the same family and share a more recent common ancestor than the hummingbird clearwing and the luna moth. The hummingbird clearwing and the luna moth are in the same superfamily Bombycoidea. According to this tree, the polyphemus moth is the most closely related to the luna moth and is in the same tribe (bugguide.net).
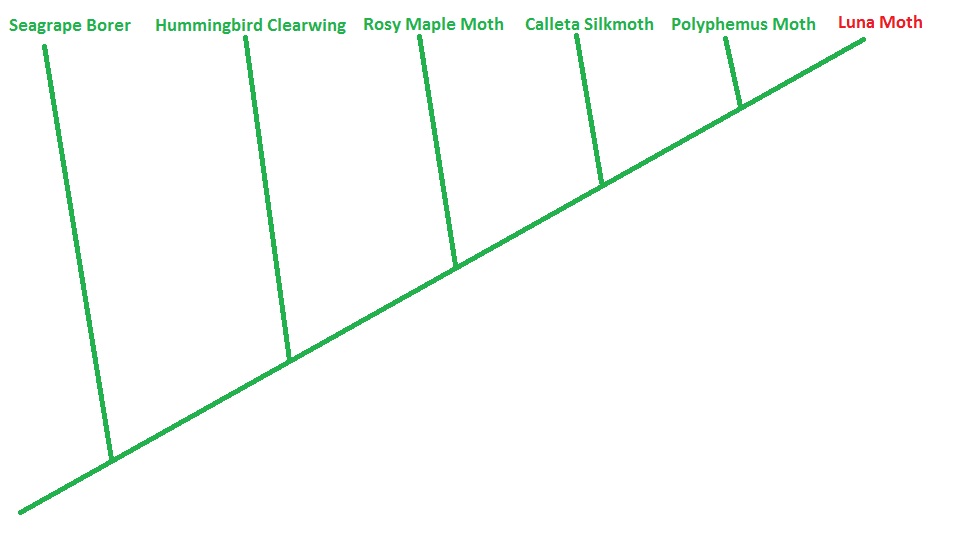
Note that phylogenetic trees can be very accurate, but are still only considered a hypothesis. Meaning although there has been an exponential amount of evidence, research, and support for the patterns of these trees, they are not set in stone and can easily change with a new discovery!
To link back to the luna moth Homepage, click
here.
To learn more about the interactions of the luna moth with other
organims, click here.
To find out where you can spot a luna moth, click
here.
To view the gallery, click here.