Classification
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Anthropoda
Class: Insecta
Order: Coleoptera
Family: Silphidae
Genus: Nicrophorus
Species: N. americanus
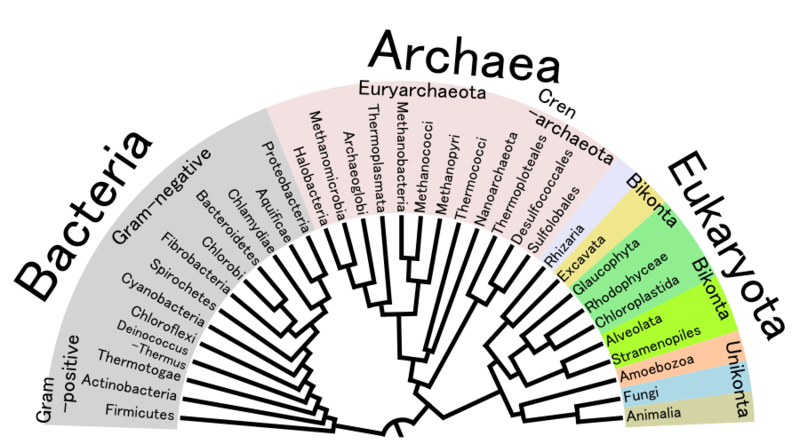
This phylogenetic tree represents relationships between the three domains: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryota. Depending on how much in common these organisms have determines how close they are on the tree. Nicrophorus americanus belongs in the domain Eukaryota under the kingdom Animalia

This phylogenetic tree shows how the American burying beetle is related to other beetles belonging to the family Silphidae.
The Domain Eukaryota:
Organisms that belong to the domain Eukarya are composed of eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus and have membrane bound organelles. The domain Eukarya includes protists, fungi, plants, and animals.
The Kingdom Animalia:
The kingdom Animalia is a major group of eukaryotic organisms and is also referred to as Metazoa. Organisms belonging to this kingdom are both heterotrophic and multicellular. Heterotrophic organisms obtain nutrients by ingestion and use organic carbon for growth. Organisms from the kingdom Animalia also do not have cell walls and are motile, meaning they can eventually move on their own by either flagella, cilia, or proteins. Some examples of organisms belonging to the kingdom Animalia are the cadisfly, orangutan, and the sea otter.
The Phylum Arthropoda:
Organisms that belong to the phylum arthropoda include insects, arachnids, and crustaceans. The word Arthropoda derives from the Greek words “joint” and “leg”. Arthropods have an exoskeleton made of chitin and have bodies that are segmented. The phylum Arthropoda is the largest and most diverse with well over a million species. A few examples of these include the tarantula, the mayfly, and the lobster.
The Class Insecta:
The class Insecta is the largest of the phylum Arthropoda. There are
over one million species and they represent over half of all known
living organisms and 90% of the kingdom Animalia. Organisms in the
class Insecta have a three part body, three pairs of jointed legs
and a pair of antennae. Check out some of these organisms that also
belong to the class Insecta:
Asian Ant,
fire fly, and the
summer
fishfly.
The Order Coleoptera:
Welcome to the wonderful world of beetles! The order Coleoptera
consists of a wide variety of beetles as there are over
300,000 species currently known. Beetles have modified wings
and their bodies consist of a head, thorax, and abdomen. Beetles are
found in many different habitats and are active in daylight and also
at night.
The Family Silphidae:
The family Silphidae are the carrion beetles. The word carrion
means dead or decaying animal flesh, which is exactly what these
beetles feed on! The family Silphidae are spread in many different
habitats, and have very distinctive antennae.
The Genus Nicrophorus:
The genus Nicrophorus have chemoreceptors on their antennae to sense
dead animals from far away. Nicrophorus are the most well-known of
the Silphidae family. They are unique insects in that both the male
and female take part in caring for their offspring.
The Species
Nicrophorus americanus:
Most commonly known as the American Burying Beetle, the species
Nicrophorus americanus is a critically endangered organsism in North
America. To learn more about Nicrophorus americanus, click on
Habitat
Back to HOME
