Interactions
Deep-sea anglerfishes like Melanocetus johnsonii have interesting interactions with other organisms. In the deeper regions of the ocean, food is often hard to come by. Therefore, anglerfish must conserve the energy that they get from their prey. Often times the next meal could be a ways away. To do this, Melanocetus johnsonii will float motionless sensing nearby prey. This organism also has bioluminescent structures that glow and lure fish and other animals within striking distance. Within the Bathypelagic region, bristlemouths and deep-sea anglerfish are the most common fish and they are typically of small size in order to reduce metabolic demand.
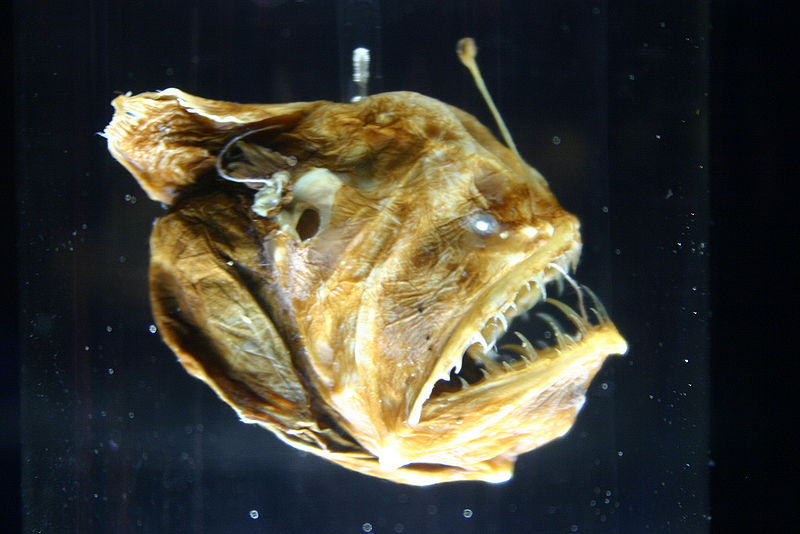
source: Ryan Somma, wikimedia commons
Most notably, Lophiformes or anglerfish
have a symbiotic relationship with bioluminescent bacteria that live
within the strand-like forms that stem from the head above the eyes.
Within this structure, these tiny bacteria these bacteria, either
Vibrio or Photobacteria, make light with the chemical
reaction:
FMNH2 + O2 + RCHO ---> FMN + RCOOH + H2O + Light(8)
With this chemical reaction, a group of luminescent bacteria will produce light in order for the anglerfish to lure prey within their range. Deep sea anglers like M. johnsonii are among the many deep sea fish that utilize this symbiotic relationship as an adaptation to the extreme environments of the bathypelagic zone and the abyssal zone.

source: Neerav Bhatt, Flickr
Continue on and learn more interesting facts about the humpback angler or go home.