Classification
Classification:
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Artiodactyla
Family: Bovidae
Genus: Madoqua
Species: Madoqua saltiana, Madoqua kirkii,
Madoqua guentheri, Madoqua piacentinii
The common name for the Madoqua is the dik-dik, which
is described as a small antelope.
Eukarya: The dik-dik is a eukaryote with cells
having nuclei.
Animalia: The dik-dik is multicellular, motile
(at least at some stage), heterotrophic, and they also lack cell
walls for structure.
Chordata: The dik-dik is bilaterally symmetric,
triploblastic, a deuterostome, and contains a notochord.
Mammalia: The dik-diks have many features that
classify them as a mammal; a couple of them are as follows:
endothermic, amniotes, covered in hair, placentals, and females
contain mammary glands.
Artiodactyla: (even toed ungulates [hooved
animals]) The weight of the Dik-dik is spread evenly about the
third and fourth toes rather than mostly on the third toe.
Bovidae: The dik-dik’s have many of the common
traits of bovids including; four-chambered ruminants, unbranched
horns (on males). Members of this family include; antelopes,
gazelles,
sheep, goats, and
cattle.
Medoqua: This is known as the dik-dik
which is a small antelope with an elongated snout forming into a
proboscis.
(Madoqua kirkii, 2013)
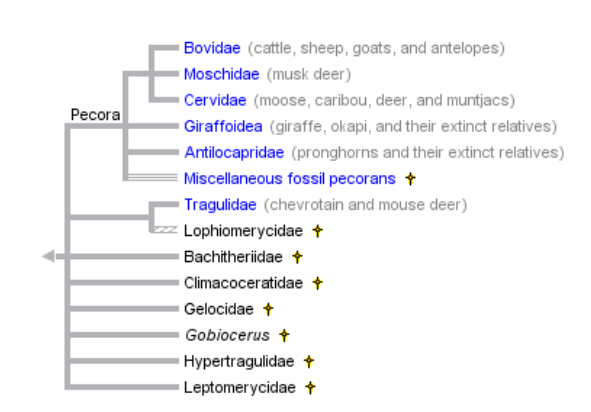 Figure 1. Phylogentic tree at the
Family level of classification emphasizing ruminants.
Figure 1. Phylogentic tree at the
Family level of classification emphasizing ruminants.
The blue families of this phylogenetic tree
are all ruminants. The Dik-dik is in the Bovidae family. This tree
shows that Moschidae and Cervidae along with the Bovidae form a
clade, and they would all be sister taxa. Because of the Tragulidae
family, the ruminants are not a monophyletic group. This tree is
based on morphological data.
(Ruminantia, 2006)
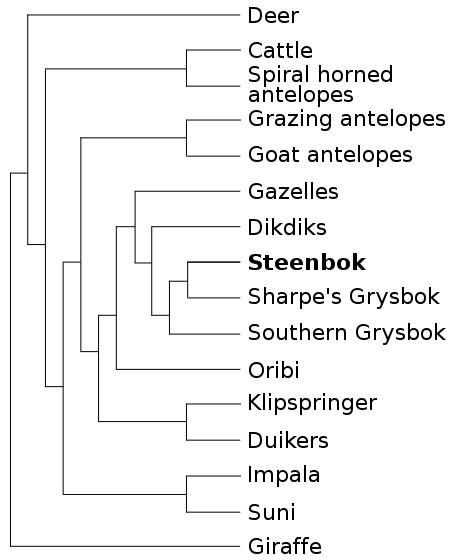 Figure 2. Phylogentic tree based
on molecular evidence
Figure 2. Phylogentic tree based
on molecular evidence
This tree shows that Dik-diks form a
monophyletic group with Gazelles, Sharpe’s Grysbok, Southern
Grysbok, and the Steenbok. The Dik-dik is more closely related to
the Steenbok and Grysboks than to Gazelles. This tree is based off
of molecular data using the following genes; Thy, PRKC1, SPTBN1,
Kap-cas, Cyt b, 12S rRNA, 16S rRNA. Four of the genes are
independent DNA markers and three are mitochondrial DNA markers.
(Matthee & Davis, 2001)
