The White-Tailed Deer
Interactions
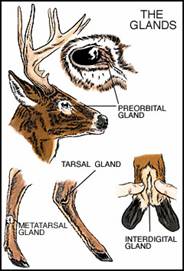
“Whitetails have four sets of external glands that are used primarily for communication.Gland secretions can describe a deer's social status, breeding condition and health. The most recognized glands are the tarsal and metatarsal glands, located on a deer's hind leg. The tarsal gland, located on the leg's inner surface, serves to identify individuals. The metatarsal gland, found lower on the leg and on the outside, may help in regulating the animal's body temperature. Interdigital glands, located between the hooves, probably leave scent trails for other deer to follow. Pre-orbital glands function as tear glands and may relay sex and social hierarchy when rubbed on branches” (mdc.mo.gov).
Some forms of deer communication when a deer is alarmed or nervous it will stomp in front feet into the ground. Another way deer communicate is by waving their tail up into the air “flag”. Deer will also snort and whistle out of their snouts. One interesting thing I found was that does will run with their tail in the air so their young can follow her easier.
Deer also interact with lungworms, footworms, liver flukes and tapeworms. Some of these are parasitic and some have a mutualistic relationship with the deer. Deer have interactions with other animals in the wild some friendly and some not so friendly. Deer are prey to the grey wolf, coyotes, bear, and cougar and mountain lion. Although the deer are in competition with other animals humans might be there largest threat. Overpopulation of humans and deer cause more and more interactions every year. Some consider the deer as pests or nuisances they get into gardens eat from fruit trees and farmers have the biggest concern with them.
Another big threat to the deer population is a nervous system disease what's known as CWD (chronic wasting disease). This fatal nervous system disease is thought to NATURALLY infect white-tailed deer, mule deer, moose and elk. It belongs to the family of diseases known as transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (TSE) or prion diseases. Deer that are infected with CWD constantly drink water, urinate, some treble or shake, some foam out of the mouth thick mucus. In 2002 was the first year of a reported case of CWD in Wisconsin .