Neisseria Meningitidis


 What
is Neisseria Meningitidis!?
What
is Neisseria Meningitidis!?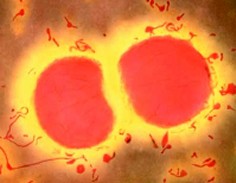
Neisseria Meningitidis is non motile and is transferred among people via direct contact with bodily fluids in which the bacteria has inhabited. This bacteria has also been found to be oxidase positive which means it contains the enzyme cytochrome c oxidase and is capable of using oxygen for energy via an electron transfer chain. Since N. Meningitidis is oxidase positive it means it is aerobic.
The fact that N. Meningitidis is known for its role in bacterial meningitis it is known as a pathogen. This bacteria lives in the mucous membranes of humans as a parasite. It has been responsible for many epidemics across the world and there have been many deaths associated with these epidemics.
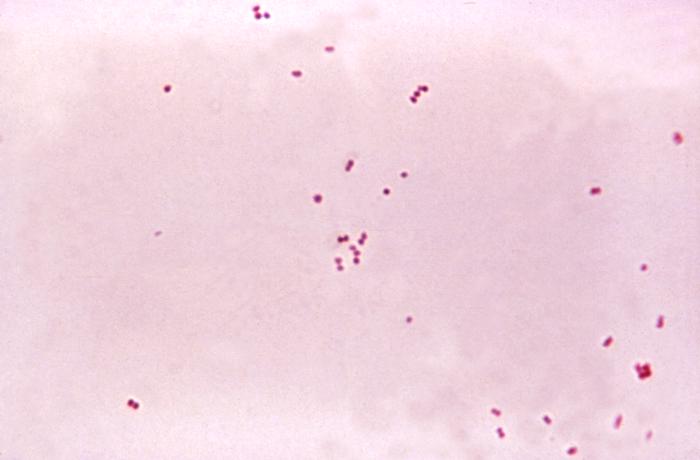
This is a photo of N. Meningitidis grown on an agar plate in a laboratory setting.
Would you like to learn more about Neisseria Meningitidis?!?! Check out its Classification and Lineage!
multipleorganisms.net