Reproduction Through a Tick Vector
THE TICKS:
Rickttsia ricketsii
has to be within a host cell
to survive and reproduce. The American dog tick (Dermacentor variabilis)
and
|
|
Located east of the Rocky Mountains |
| and sometime along the Pacific Coast. |
THE LIFE CYCLE:
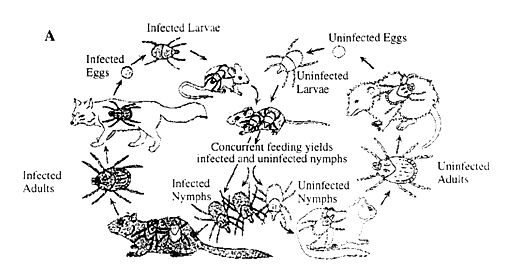
HOW THE TICKS CAN GET INFECTED:
-
R. rickettsii gets into the tick through consumption of blood of an infected animal; animals can get infected through eating infected food.
-
Male ticks can transfer R. rickettsii to females during the mating process.
-
When R. rickettsii get into the cell, of any host, it uses binary fission to reproduce and infect more cells within the host.
Then a female tick can transmit R. rickettsii to her eggs once infected. As the infected tick eggs continue to grow, R. rickettsii may be transmitted to the second host during the feeding process. R. rickettsii is transmitted to a vertebrate host, which could take hours of attachment, through saliva while feeding on it. Once infected, the tick can carry the R. rickettsii for life.
Find out what happens after Rickettsia rickettsii get into the host