Adaptation and Interactions
Pediculus humanus is found on the bodies of humans. Whether this organism is found on the head or the body of the human, greatly depends on the sub-species. These two species include Pediculus humanus corpis, body louse, and Pediculus humanus capitis, found on the human head. It is most common to find lice on the human head, along the scalp. Many times, you will find head louse behind the ears, along the hair line, on a person's head.
Once a human notices these
insects, many try to get rid of them as soon as possible.
People will go through any
 process
to get rid of these nasty creatures. What many people don't
know is that human lice are resilient. Special shampoos
and conditioners,
combs,
hair treatments, etc are advertised to eliminate the lice from the
hair and scalp. It is found that lice can adapt to their
surroundings and close down their system so they are not affected by
these treatments. Although they can not disregard all of these
treatments, they seem to linger around the human many days after the
use of shampoo. It has been found that the chemicals that are
used in various treatments seem to be quite similar with one another. So, if
lice is resistant to one type of treatment, they seem to become
immune to all. One treatment that doctors have found to be the
most effective is "HairClean 1-2-3", which is found 98% effective.
This product uses natural oils, as opposed to the usual chemicals,
to eliminate the head lice. It has been proven that
natural oils will significantly work better than the chemicals
because the lice are more prone to become resistant to them.
process
to get rid of these nasty creatures. What many people don't
know is that human lice are resilient. Special shampoos
and conditioners,
combs,
hair treatments, etc are advertised to eliminate the lice from the
hair and scalp. It is found that lice can adapt to their
surroundings and close down their system so they are not affected by
these treatments. Although they can not disregard all of these
treatments, they seem to linger around the human many days after the
use of shampoo. It has been found that the chemicals that are
used in various treatments seem to be quite similar with one another. So, if
lice is resistant to one type of treatment, they seem to become
immune to all. One treatment that doctors have found to be the
most effective is "HairClean 1-2-3", which is found 98% effective.
This product uses natural oils, as opposed to the usual chemicals,
to eliminate the head lice. It has been proven that
natural oils will significantly work better than the chemicals
because the lice are more prone to become resistant to them.
The interaction concept of these creatures is quite simple. They obviously spend their whole life, interacting with their host, the human. This, once again, is because they rely on the human blood for nutrition. Since they are living on the human, their interactions are parasitic. This is because their are benefiting from the nutrition provided by the human, while the human tends to suffer. Humans will experience an uncomfortable itching sensation from the sucking of the blood and living on the human, itself. On the other hand, there has not been many studies on how lice act towards one another, or how they compete for blood from the host.
 As
the louse feeds on its host, the human, it must have some sort of
transportation. Just like any other insect, Pediculus
humanus travels amongst its host by their six legs. They
use these legs to get to a specific location on the head, body, or
pubic area to feed. Not only are legs an important factor, but
their mouth and claws contribute to obtaining their
nutrition. These structures play a
significant
As
the louse feeds on its host, the human, it must have some sort of
transportation. Just like any other insect, Pediculus
humanus travels amongst its host by their six legs. They
use these legs to get to a specific location on the head, body, or
pubic area to feed. Not only are legs an important factor, but
their mouth and claws contribute to obtaining their
nutrition. These structures play a
significant
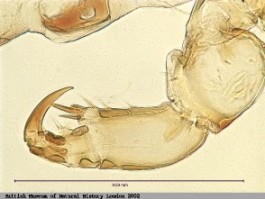 role
to attach to the human and suck in the blood. As you can see
in the image to the right, the claws are found to have and dominant
claw, along with two to three smaller ones. This provides a
firmer and more promising grip onto the scalp or body of the host.
role
to attach to the human and suck in the blood. As you can see
in the image to the right, the claws are found to have and dominant
claw, along with two to three smaller ones. This provides a
firmer and more promising grip onto the scalp or body of the host.
The environmental stimuli of human lice are found to be very aware of their surroundings. This, once again, deals with the various treatments that people undergo to get rid of these little pests. Lice can adapt to many treatments and alter their lifestyles, in order to survive. So, please be aware that these lice are more intelligent than you may think!
Enough of this, give me some tasty facts on such creepy crawlers!