Where do I Belong?
The Classification of Human Lice
Pediculus humanus was discovered by Linnaeus in 1758. The common name, referred to by many, is human lice.
Domain: Eukarya
Eukarya is one of the three domains, Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya. This domain has eukaryotic cells, which contain membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells also have a nucleus.
Kingdom: Animalia
Kingdom Animalia contains eukaryotic cells, are multicellular and heterotrophic- get their food and energy from other organisms, motile, and lack cell walls.
Phylum: Arthropoda
Human lice fall under the phylum Arthropoda because of the following characteristics:
~Triploblastic: embryos contain three different types of tissues or germ layers, the endoderm (digestive tract), mesoderm (muscle, bone, circulatory system), and ectoderm (skin and nervous system).
~Coelomate: presence of a fluid-filled body cavity that creates a medium for circulation, along with space for internal organs.
~True digestive system: contain both a mouth and an anus.
~Bilateral symmetry: single plane of symmetry that allows for cephalization. This lead to the evolution of a head or anterior region and the development of structures for feeding, sense of the environment, and the ability to process information.
~Segmented bodies.
~Exoskeleton composed of chitin, providing support and protection.
~Paired, jointed appendages.
~Grow by molting, meaning they shed the exoskeleton to grow.
Class: Insecta
The class Insecta is the most diverse group of animals on Earth. These animals obtain compound eyes, three pairs of legs (six legs), are dioecious (separate sexes), and their bodies consist of a head, thorax, and abdomen. Other classes within the Arthropods include: Crustacea, Myriapoda, and Chelicerata. These organisms differ from the Insects based on the number of legs, tagmeta (regions), wings, and pairs of antennae. Crustacea obtain five pairs of legs or more, two body regions, two pairs of antennae, and are wingless. Myriapoda have numerous amounts of legs, two body regions, one pair of antennae, and are wingless. Chelicerata have four pairs of legs, two body regions, usually no antennae, and are wingless.
Order: Phthiraptera
Pediculus humanus is included in the order of Phthiraptera because they do not obtain any wings on their bodies. Their legs have special claws to attach to hosts. Other orders within the insects may include wings, large eyes, long antennae, large head, or large hind legs.
Family: Pediculidae
Human lice are classified as blood feeders. Their mouthparts include the process of piercing and sucking. Eggs are laid singly and glued to hair. Families, aside from Pediculidae, may be found specifically on the pubic area or facial hair.
Genus: Pediculus
Pediculus, the genus of the species, Pediculus humanus, is a general term for any lice found on a human.
Species: Pediculus humanus
Pediculus humanus is the scientific name for human lice, whether it be located on the head or pubic area.
Below shows that gradual specification, eventually leading to human lice, Pediculus humanus.
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Arthropoda
Class: Insecta
Order: Phthiraptera
Family: Pediculidae
Genus: Pediculus
Species: Pediculus humanus
Let's take a closer look at the species within the various orders, families, and genus's. Starting with the order (Phthiraptera) we will zoom in:
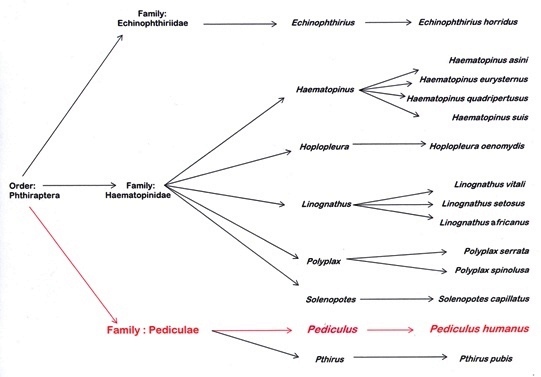
I created this phylogenetic tree using Microsoft Word. It shows the classification of Pediculus humanus. As you follow the arrows across, you can see the specific order, family, genus, and species, all based on the morphological traits at which each specie obtains. Not only does this tree show Pediculus humanus, but also the many organisms that are closely related to it. Although there are many organisms shown on this tree, they are all classified as some type of lice. What differentiates human lice from other species is the fact that they are specifically parasitic to humans. For instance, the family Echinophthiriidae deals with lice found on seals. Polyplax spinolusa is lice found on rats. Another common type of lice that humans are familiar with is Pthirus pubis, lice found in the pubic area. Some other differences among the species include their host, presence of wings or antennae, large heads, and many other traits an/or characteristics.
Click here to learn about the surroundings of these insects ....
