Classification
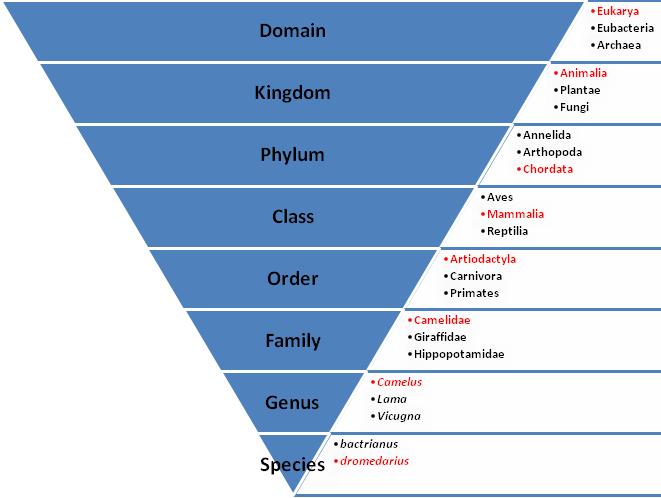
The above phylogenic tree shows the tracing of Camelus dromedarius from domain to species labeled in red.
No one taxonomy was utilized when creating this tree, however, morphology does seem to be expressed the most.
Other kingdoms, phylums, classes etc. shown were chosen for no particular reason. The three genus listed all fall under
the family Camelidae as well as the two species which fall under the genus Camelus.
Domian: Eukarya
Camelus dromedarius is under the domain Eukarya due to the fact that their cells contain mitochondria.
Kingdom: Animalia
This organism is both multicellular and heterotrophic thus falling under the kingdom Animalia.
Phylum: Chordata
The Arabian camel has both a dorsal nerve cord and a notochord, therefore it belongs to the phylum Chordata.
A dorsal nerve cord is nerve fibers bundled together that follow the "back" such as the spinal chord in humans.
A notocord is a support structure made of cartilidge that runs beneath the nerve cord.
Class: Mammalia
The presence of hair and mammary glands places Camelus dromedarius within the class of Mammalia.
Order: Artiodactyla
Artiodactyla means "even-toed" which correlates with the foot of the camel.
Family: Camelidae
The dromedary camel fits into the family Camelidae based on the how it bears its weight on its feet and includes the camels, lamas, and vicugna.
Genus: Camelus
The dromedary camel's toes are fused together forming a pad therefore it is catagorized in the Camelus genus.
Species: dromedarius
The species dromedarius separates Camelus dromedarius from its relative Camelus bacterian which has two humps.
Scientific Name: Camelus dromedarius
Common Names: Camel, One-humped Camel, Dromedary, Dromedary Camel, and Arabian Camel


