Mexican Axolotls or "Mexican walking fish"
| Domain | Eukarya |
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Amphibia |
| Order | Caudata |
| Family | Ambystomatidae |
| Genus | Ambystoma |
| Species | Ambystoma mexicanum |
Domain
Eukarya- The Mexican Axolotl is classified under Eukarya for many reasons, all species under the domain Eukarya posses cells that contain a true nucleus bounded by a nuclear membrane. Organisms that are make up the Eukarya also contain membrane-bound organelles.
Kingdom
Animalia- The Mexican Axolotl falls under the kingdom Animalia because they are multicellular. Animals are heterotrophic, meaning they must get their food by eating other organisms. Also all animals require oxygen for their metabolism, can sense and respond to their environment, and have the capacity to reproduce sexually.
Phylum
Chordata- Chordata is a group of animals that are linked due to five common attributes at some point in their life: a notochord, a hollow dorsal nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, an endostyle, and a post-anal tail.
Class
Amphibia- Axolotls belong to the class Amphibia because they do not have amniotic eggs, they are cold-blooded and they have the adaptation of gills for respiration. Other members include frogs, toads, newts, and caecilians.
Order
Caudata- Axolotls fall under the this order due to them having a tail with two pairs of limbs. Members of this the order caudata also have elongated bodies and are usually found in aquatic environments. Paedomorphosis, the retention of larval characteristics throughout entire life, is a common feature that sets this order apart from others.
Family
Ambystomatidae- The family of Amphibians that include the Axolotls. The ambystomatidae family are characterized by their broad heads, costal grooves down the body, a compressed tail, a complex pattern of spinal nerves, and the ability to regenerate lost limbs, tails, and organs.
Genus
Ambystoma- or (mole salamander), are salamanders that possess gills and have an aquatic life without developing in an adult form.
Species
Ambystoma mexicanum- The Mexican Axolotl is an aquatic salamander that are paedomorphosis. They possess external gills and a finned tail for swimming. The A. mexicanum is used as a model organism for many research studies.
Phylogenetic Tree
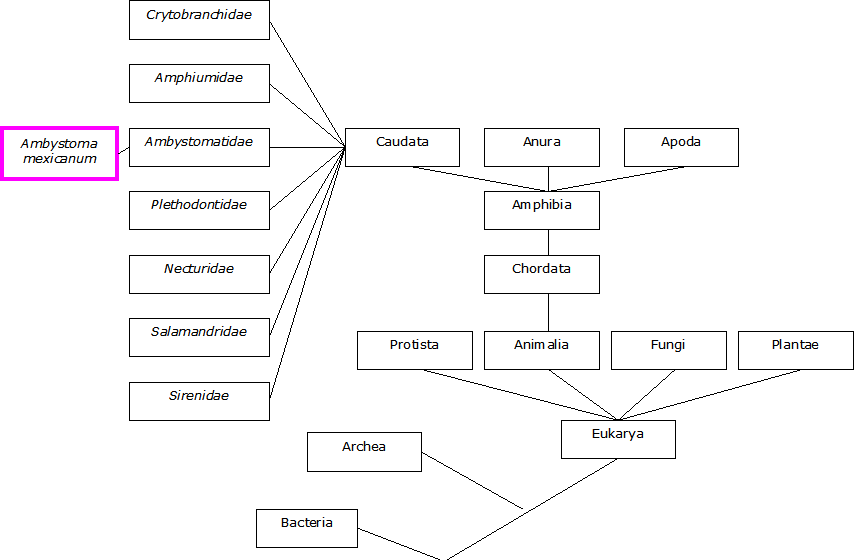
Phylogenetic Tree created by Britni Osuldsen
The phylogenetic tree shows the relationship that the Ambystoma mexicanum has to other families located under the order of caudata. Along with how it traces back to common ancestors.

