Classification
Scientific Origins
According to Grant Hutchinson, anesthetist and writer for the British Medical Journal, The word Toxoplasma originated from the Greek word toxon, which meant "bow." This became the basis for the Latin word toxicum, which meant "poison." The original Greek meaning is the one used for the word Toxoplasma, meaning "bow shaped organism (2)."
According to Freij et. al. in Toxoplasmosis, the word gondii is the name of a North African desert rodent which is related to the organism that T. gondii was originally found in (3).
Classification
Domain: Eukarya; T. gondii is a single celled organism that contains a nucleus and has membrane bound organelles.
Kingdom: Alveolata; This group contains protozoa that were found to have a common ancestor 900 million years ago. This precursor had structures that are now homologous between all members of this group. This system allows for a monophyletic grouping of organisms. An older system used "Protists" as an artificial dumping ground kingdom which contained many paraphyletic groups.
Phylum: Apicomplexa; Members of this group have highly developed structures at their anterior regions called apical complexes, which are used in host cell invasion.
Class: Coccidia; Members of this group are obligate intracellular parasites. They generally complete the sexual stage of their life cycles within a host's intestinal tract.
Order: Eucoccidiorida; Members of this group contain parasites of humans, domesticated animals, wild animals, and birds.
Family: Sarcocystidae; These group members carry out a life cycle that requires more than one obligatory host. The hosts themselves usually participate in a predatory/prey relationship. Oocysts are passed between them through feces.
Genus: Toxoplasma; This genus requires transmission between a member of the felidae and the rodents to carry out its sexual life cycle.
Species: Toxoplasma gondii; This is the only species in the genus Toxoplasma.
Classification information found in the NCBI (4).
Phylogeny information found in the Tree of Life Project.
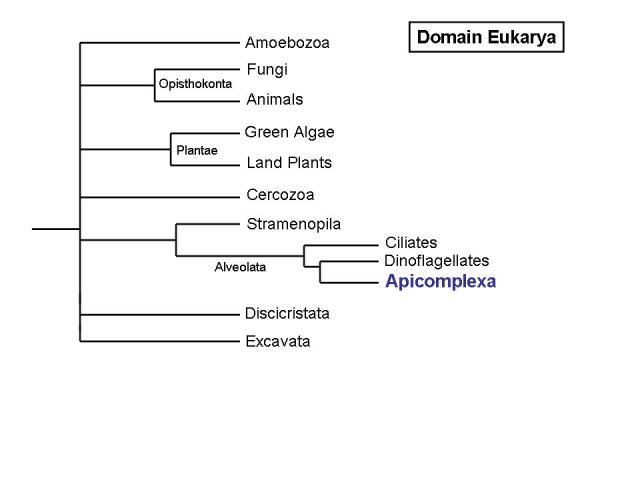
This phylogenetic tree is based on small subunit rRNA. The molecular data confirmed an older system based on morphologies. Each group represented is a monophyletic group that can be traced back to a common ancestor. Evolutionary data is not represented since researchers are still deciding which group would have been the most ancient lineage. This tree shows that T. gondii, a member of the Apicomplexa, was closely related to the Dinoflagellates. In fact, the kingdom Alveolata can be traced back to a common ancestor 900 million years ago that had homologous structures of all the Alveolata. This tree also gives an idea of where T. gondii fits in the larger picture of phylogeny. The domain represented is Eukarya out of the the other two: Prokarya and Archaeya (4,5).