Interactions
The Dungeness crab has several interactions
with many marine species, but the most important is their
interaction with humans.
Marine
Interactions
Nadelspora canceri, a
microsporidian
Nadelspora canceri is a parasite to
the Cancer magister, and also the most pathogenic
parasite of crustacean diseases. In this
interaction the Cancer magister acts as the host to this
parasite.
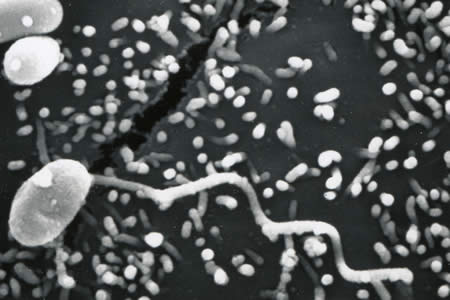 The parasite infects the muscle tissues
which causes a white discoloration in the muscle and ultimately
leads to muscle destruction.
The parasite infects the muscle tissues
which causes a white discoloration in the muscle and ultimately
leads to muscle destruction.
The prevalence of infected crabs can range
from 1.4% to 48% depending on the collection site.
The highest concentration of infected crabs was found in
estuaries, and it was more prevalently found in younger 1 to 2 year
old crabs.
Chlamydia-like
bacteria
This Chlamydia-like organism is a
Gram-negative bacterium that infects the gills of the crab.
It was responsible for extreme mortality in Willapa Bay, WA
in the 1980s.
Dr. Sparks discovered that the
disease occurred only in local crab population in winter and
spring. It is believed to
be only prevalent
during extreme cold weather which suppresses the crabs immune
system.
Common
Predators
Nemertean worm, Carcinonemertes errans:
This worm commonly eat the eggs of
the Dungeness crab
halibut, dogfish, sculpins,
octopus,
and
sea otters




Human Interactions
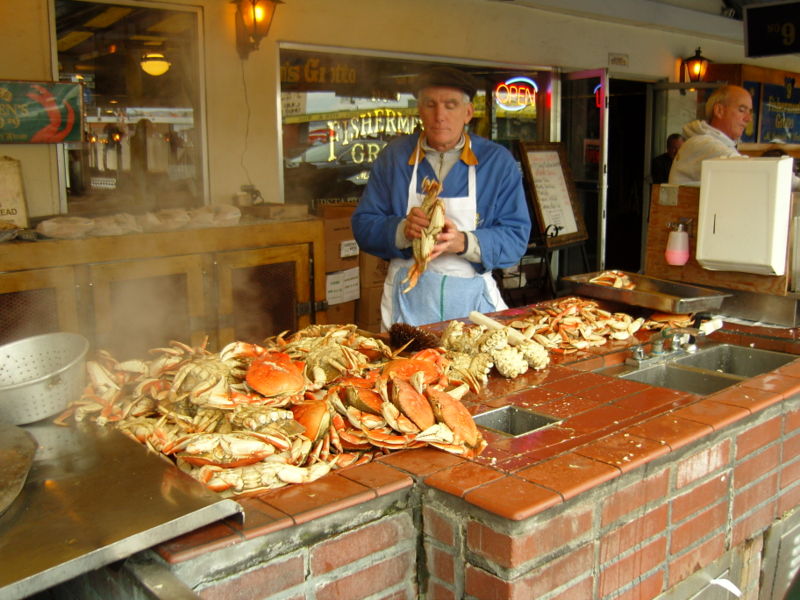

Crab fishing is a multi million dollar
industry and many west coast communities economies are based on
the years harvest. This is why the Cancer
magister is such an important organism because many people
rely on the population of this organism. In
Oregon
alone each fishing boat can be carrying a value ranging from
$5 million to $44 million alone, showing just how prized these
crabs are.
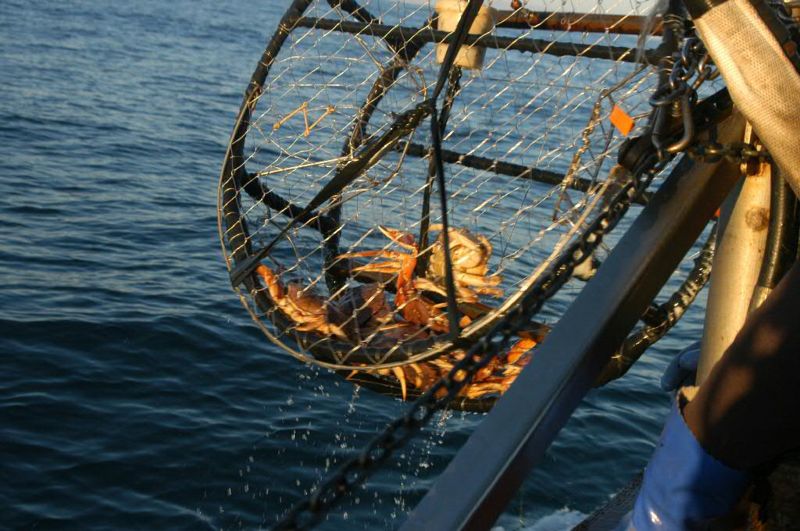

Each year the Dungeness crab population is
fully exploited, 80-90%
of all available legal sized males are
caught. Since females are illegal to catch,
the population still can be sustained by the ability to mate
with younger males and sustain the population.
Last, check out
the Interesting facts of
the Dungeness crab.

 The parasite infects the muscle tissues
which causes a white discoloration in the muscle and ultimately
leads to muscle destruction.
The parasite infects the muscle tissues
which causes a white discoloration in the muscle and ultimately
leads to muscle destruction.





