Classification
How did the watermelon get its common name?
The C. lanatus produces a fruit that is about
93% water, making it the majority of it water, hence the name “water”
melon. The “melon” part came from the fact that the fruit is large and
round and has a sweet, pulpy flesh.
Citrullus lanatus...what does that
even mean?
The scientific name of the watermelon derived from both Greek and Latin
roots. The Citrullus part comes from a Greek word “citrus”
which is a reference to the fruit. The lanatus part is Latin,
and has the meaning of being wooly, referring to the small hairs on the
stems and leaves of the plant.
Scientific Classification


Domain- Eukarya
Kingdom- Plantae
Phylum- Embryophyta
Class- Dicotyledoneae
Order: Cucurbitales
Family: Cucurbitaceae
Genus: Citrullus
Species: C. lanatus
Domain: Eukarya
The domain Eukarya contains cells
with true nuclei, as well as membrane
bound organelles. These factors qualify it as a eukaryotic
organism. This domain covers a gigantic variety of organisms
ranging from uni-cellular protists to large animals such as the
orangutan.
Kingdom: Plantae
Plantae is the kingdom with multi-cellular organisms
that have cells with cell walls made of
cellulose. Cells also have chloroplasts allowing them to
photosynthesize, meaning they gain nutrition by energy from sunlight
and water. Plantae is a kingdom that includes a wide variety of
organisms as well. Another organism within this kingdom is much
larger than the Citrullus lanatus and goes by the
common name,
the white willow.
 Phylum: Embryophyta
Phylum: Embryophyta
The Citrullus lanatus is under the phylum
Embryophyta because it
is a land plant, located terrestrially. In addition, it contains
seeds, also known as embryos. Another common organism from this
phylum includes the
cabbage palm.
Class: Dicotyledoneae
The class Dicotyledoneae has all vascular plants;
and more specifically dicots, meaning their seeds typically has two outer shell coverings.
Order: Cucurbitales
Cucurbitales is the order containing
flowering plants unisexual flowers.
Family: Cucurbitaceae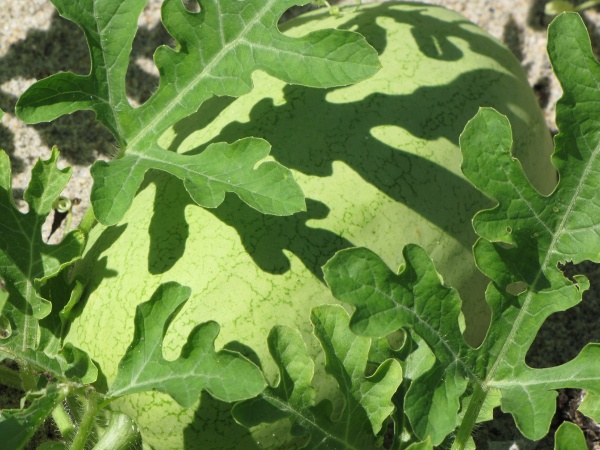
The family Cucurbitaceae has plants
with sprawling herbaceous vines and melons. A
melon is a large fruit with a fleshy inside and hard, protective
skin. This family is also known as the gourd family. Other
members within this family include the cantaloupe,
squash, and
pumpkin.
Genus: Citrullus
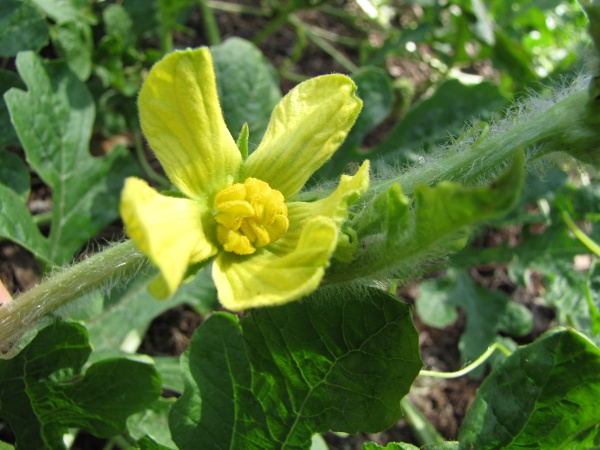
The Citrullus lanatus is under the genus
Citrullus because it is
a desert vine and native to Eurasia and Africa. The flowers are
yellow and the seeds are somewhat flattened. This genus contains
a total of 4 species including
C. colocynthis, C. ecirrhosus,
C. lanatus, and C. rehmii.
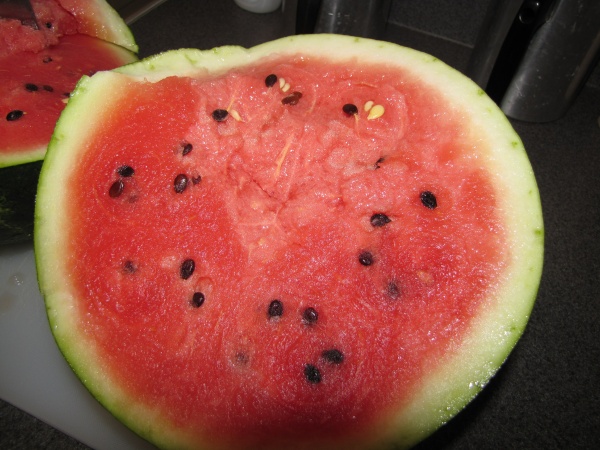
Species: C. lanatus
The watermelon is given the name lanatus because of its
pink/red or yellow flesh and black seeds, along with all
of the above characteristics.
Phylogeny
Below is a phylogenetic tree, demonstrating
the broad classification of the Citrullus lanatus
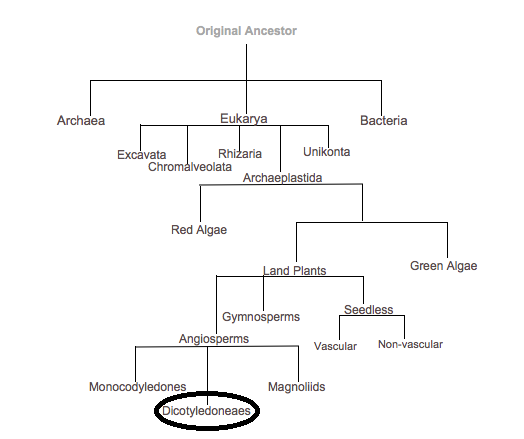
Information modified from Campbell and Reece,
Biology textbook 8th edition
The above phylogenetic tree is based off of morphological features.
It is a very general classification which starts out as broad as the
domains and leads into the class where the Citrullus lanatus
resides. The three domains of life include Archaea, Eukarya, and Bacteria. As
explained above, the Citrullus lanatus belongs under the group
Eukarya, which is broken down into 5 super-groups. Archaeplastida is the
super-group land plants fall under and is ultimately where the kingdom
Plantae comes from. The land plants are broken down into 4 groups,
angiosperm being the type of plant of the Citrullus lanatus.
Finally, the Angiosperm phylum is broken down into 3 classes:
Monocodyledones, Dicotyledoneaes, and Magnoliids. Again, from the
classification information above, the Citrullus lanatus is part
of the Dicotyledoneaes class for evidential reasons.
Here is another phylogenetic tree representing
a closer look at the family of the watermelon: Cucurbitaceae
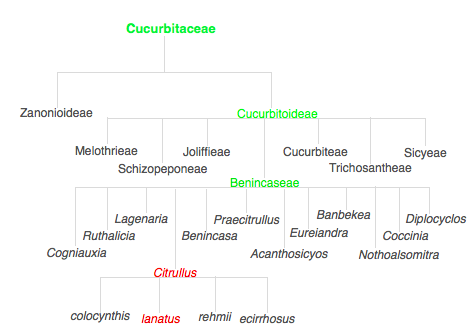
Information modified from
myetymology
This phylogenetic tree is much more specific than the first one
as it morphologically compares the Citrullus lanatus to other members
within its family, Cucurbitaceae. The family Cucurbitaceae is made up of
two subfamilies: Zanoioideae and Cucurbitoideae. The sub-family
Cucurbitoideae is made up of all food producing plants. It has 7 “tribes” including the one the Citrullus lanatus
falls under called the Benincaseae. There are 12 genera members of this
tribe, Citrullus being one of them. Finally, like stated above, the
genus Citrullus contains 4 species, including lanatus, also known as,
the watermelon.
Find out where in the world you can find the Citrullus lanatus under habitat/geography!



