
Who Are You?!

Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom:
Plantae
Phylum:
Magnoliophyta
Class:
Magnoliopsida
Order:
Rosales
Family:
Rosaceae
Genus:
Malus
Species:
Malus domestica
Eukarya- Is a domain of organisms that are
classified by the presence of membrane bound organelles and true
nucleus. Eukaryotes are also bigger and more complex than
Prokaryote (usually!).
Plantae- Is a kingdom of organisms that are
multicellular, autotrophic organisms that contain cell walls
made of cellulose.
Magnoliophyta- This phylum includes all
flowering plants
Magnoliopsida– Is a class that includes
organism that are Dicotyledonous (Dicots). Dicots have
net-like vein leaves, two cotyledons, a taproot, and floral
organs that are in multiples of fours and fives.
Rosales – This order is largely based on
phylogenetic analyses of DNA sequences.
Rosaceae – Is a family of trees, shrubs, and
herbs. They have medium-sized flowers that have five sepals
fused at their base.
Malus – This genus contains small trees or
shrubs that are deciduous and grow apple fruits.
Phylogeny
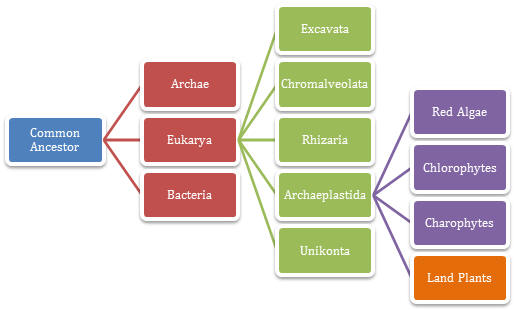 This phylogenetic tree on the right shows the grand scheme of
things. It follows Malus domestica’s most general
classification from its domain to kingdom. On the left, you see
blue common ancestor that all living things derive from. From
there, all living things are divided into 3 domains seen in red.
Then, the domain Eukarya is broken into 5 supergroups shown in
green. Lastly, the supergroup Archaeplastida is divided
into 4 kingdoms shown in purple. Malus domestica would finally
be classified under the kingdom land plants. Chlorophytes and
Charophytes are classified together as green algae and it is
believed that green algae gave rise to land plants.
This phylogenetic tree on the right shows the grand scheme of
things. It follows Malus domestica’s most general
classification from its domain to kingdom. On the left, you see
blue common ancestor that all living things derive from. From
there, all living things are divided into 3 domains seen in red.
Then, the domain Eukarya is broken into 5 supergroups shown in
green. Lastly, the supergroup Archaeplastida is divided
into 4 kingdoms shown in purple. Malus domestica would finally
be classified under the kingdom land plants. Chlorophytes and
Charophytes are classified together as green algae and it is
believed that green algae gave rise to land plants.

The
phylogenetic tree on the left shows Malus domestica’s closest
relatives. All of these species come from the genus Malus and
have a common ancestor shown in blue. All of the species in
red are different types of crabapples. Some kinds of
crabapples are able to be cross-fertilized with apples showing their
close relation. Finally, at the end there is a break between
wild apples and domesticated apples. This happened when humans
started to domesticate apples and caused two different species of
apples to form. This tree is based off of morphological
characteristics.
