Nutrition
Rhododendron ponticum is a plant; therefore, it is a primary
producer. Primary producers produce their own food through
photosynthesis. The following is the photosynthesis equation:

+ H2O + CO2 —>
C6H12O6 + O2
Photosynthesis begins with carbon dioxide from the atmosphere,
water mainly from the soil that was taken up through the roots, and
energy from the sun. These reactants form glucose and oxygen as
products. The glucose is either used for cellular respiration or
structures in the plant such as the cell walls. Oxygen is released
into the atmosphere or it is used for cellular respiration in the
electron transport chain.
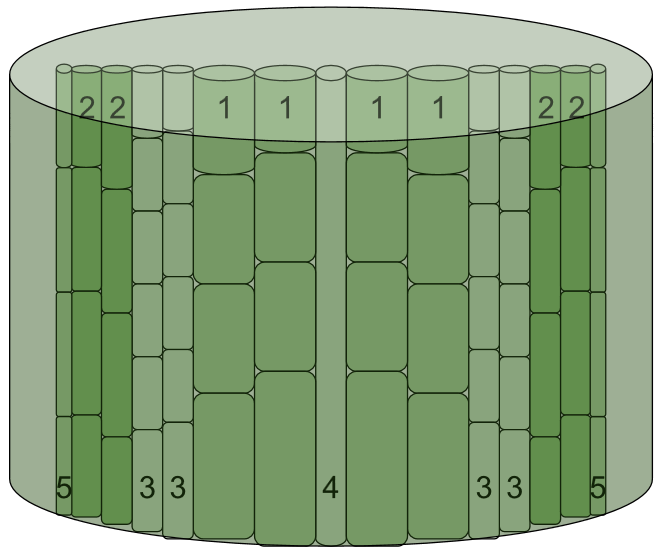
How does water and sugar move around in
Rhododendron ponticum?
Water is transported through the plant tissue in the xylem. Water is
pulled up from the roots to the top of the plant. The sugars are
pushed through the phloem from the source (leaves or storage roots)
to the sink (tissue where the sugar is used).
In this image xylem is labeled as 1 and phloem is labeled as 2. The remaining areas are cambium (3), pith (4), and companion cells (5).
©Michael Salaverry 2012
Reproduction of Rhododendron ponticum
.jpg)