Classification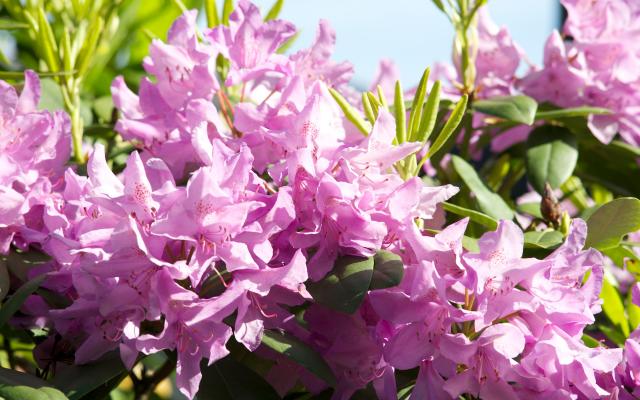
Domain - Eukarya
Kingdom - Plantae
Subkingdom - Tracheobionta
Superphylum - Spermatophyta
Phylum - Anthophyta
Class - Dicotyledoneae
Order - Ericales
Family - Ericaceae
Genus - Rhododendron
Species - Rhododendron ponticum
©Design for unity
Eukarya
This domain includes organisms which possess membrane bound
organelles and a true nucleus. Eukaryotes contain a wide variety of
organisms such as
animals,
fungi, and "protists."
Plantae
Plantae includes organisms that are multicellular and contain
cellulose in their cell walls. Also, the majority of plants are
autotrophic. Many organisms are considered plants including
liverworts, mosses, and
ginkgo
trees.
Tracheobionta
The subkingdom Tracheobionta includes vascular plants.
Vascular tissue transports water and nutrients throughout the plant.
Examples in this subkingdom include Lychophytes (club mosses, spike
mosses, quillworts), Pterophytes (ferns, horsetails, whisk ferns),
Gymnosperms, and Angiosperms.
Spermatophyta
This superphylum includes seed plants. Seed plants include
both Gymnosperms ("naked seed") and Angiosperms (such as
passion fruit).
Anthophyta
Also known as angiosperms, this phylum includes flowering
plants. The flowers' ovaries are a very important part of
development. First, the development of the seeds takes place inside
of the flowers' ovaries, and then the ovaries themselves go through
development and turn into the fruit. This includes organisms from
rose bushes to
calla lillies.
©Gary Halvorson, Oregon State Archives 
Dicotyledoneae
Dicot flowers have several unifying characteristics. They include
having two cotyledons, three pores in the pollen grain, vascular
tissues arranged in a circle, taproot systems, netlike arrangement
of veins, and flowers in multiples of four or five (tetramerous or pentamerous flowers). Examples of dicots include beans,
sunflowers,
and buttercups.
 Ericales
Ericales
This group is very diverse; therefore, there are not any obvious unifying characteristics for the Ericales.
However, most members, including Rhododendron ponticum,
have radially symmetric flowers with pedals that are weakly fused
together. Also, they have chemicals that are often used for protection from herbivores. Examples of Ericales would be
pitcher
plants and
kiwifruit.
Ericaceae
Ericaceae, also known as the heath family, is also very
diverse. Although there are exceptions, the majority of plants
classified under Ericaceae, including Rhododendron ponticum,
are associated with
fungi in their roots and are seriously invasive. An exception to
this is
the
blueberry bush,
an edible fruit.
Rhododendron
This genus includes evergreen and deciduous shrubs with
funnel shaped flowers and elliptic leaves. This genus also includes
Azaleas.
Rhododendron ponticum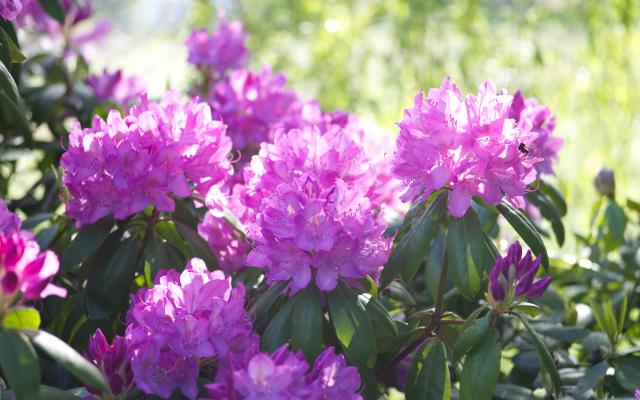
Rhododendron comes from the Greek
language. 'Rhodos' means 'rose' in English and 'dendron' means
'tree.' The name 'rose tree' seems very appropriate based off of the
physical characteristics of Rhododendron ponticum. Rhododendron
ponticum has large clusters of colorful flowers and is a woody plant.
‘Pontic’ refers to the type of Greek language, Pontic Greek,
spoken in regions on the southern shores of the Black Sea which is
where this species is native to.
©Design for unity
Its common name, Rhododendron, is simply its genus.
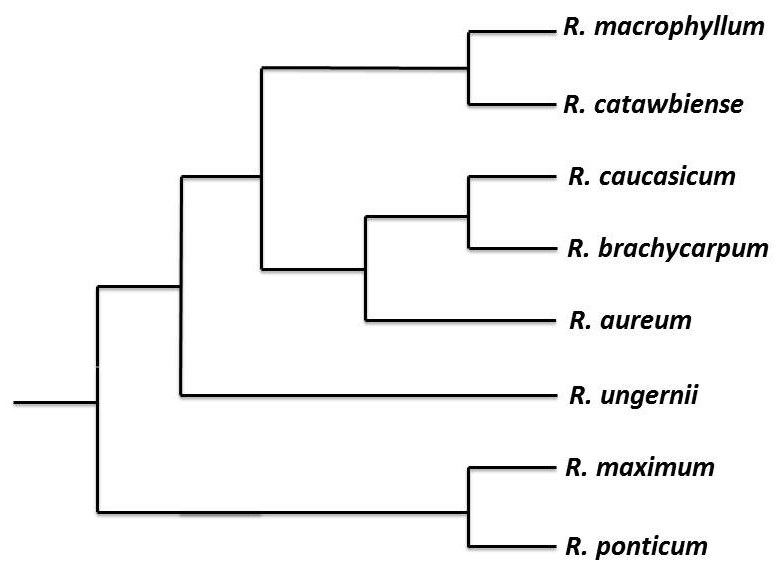 The image to the left is of a monophyletic tree showing Rhododendron
ponticum and its closest relatives. All species are a part of
the genus Rhododendron, subgenus Hymenanthes, and
subsection Pontica. It is estimated that there are over
1,000 different species of Rhododendron in the world.
The image to the left is of a monophyletic tree showing Rhododendron
ponticum and its closest relatives. All species are a part of
the genus Rhododendron, subgenus Hymenanthes, and
subsection Pontica. It is estimated that there are over
1,000 different species of Rhododendron in the world.
As the tree shows, Rhododendron ponticum is closest related to Rhododendron maximum. Its next closest relative is Rhododendron ungernii.
The image to the right is also showing a monophyletic tree that helps to show where Rhododendron ponticum is classified. Rhododendron ponticum is under the domain Eukaryote and super-group Archaeplastida.
In the image displayed, the kingdom Rhododendron ponticum is classified under is circled in green. As explained above, Rhododendron ponticum is a plant. According to the tree, land plants are most closely related to charaphyceans which is a green algae.
The image to the left goes into greater detail concerning how the kingdom land plants is broken up. Angiosperm, which Rhododendron ponticum is classified under, is circled and is closest related to the gymnosperms.
.jpg)

_(clacDA0006a)[1].jpg)
.jpg)
