Proud Parent of Identical Twins
Plesiomonas shigelloides reproduces via binary fission. This is a form of asexual reproduction in which an individual parent cell splits into two identical daughter cells that are clones of the parent cell. Mutations or mistakes can occur during the DNA replication, which results in different strains of the bacterium. Cells with favorable mutations for their habitat tend to do better than cells with unfavorable mutations, which will be ultimately outcompeted and killed off.
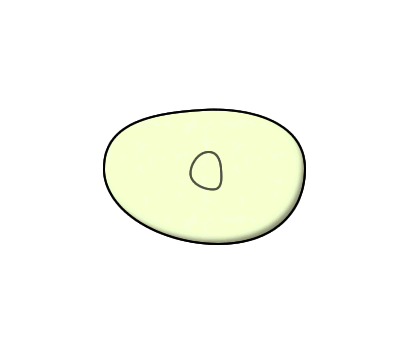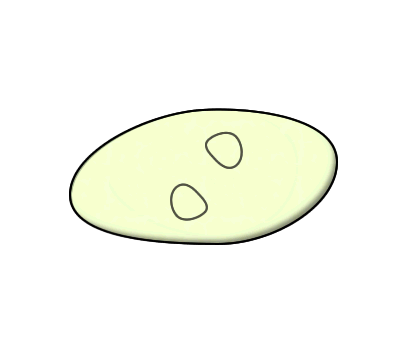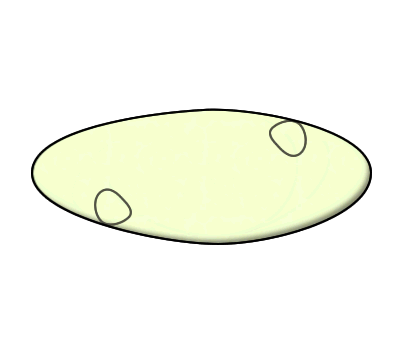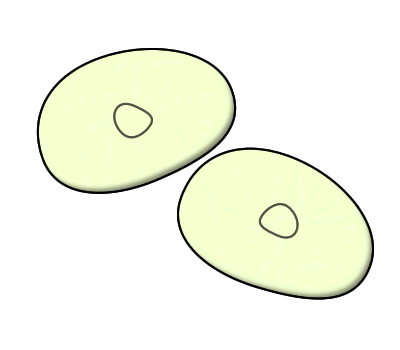
Steps of binary fission:
1. The DNA starts to replicate and the two sets start migrating towards the poles of the cells soon after replication has begun.
2. The bacterial cell elongates as DNA replication continues and the two sets are moving to the separate poles.
3. The plasma membrane grows pinching the cell down the center.
4. Two identical daughter cells are produced.
Though Plesiomonas shigelloides has not been observed to swap genetic material, other bacteria, such as E. coli have been observed to transfer genetic material if environmental conditions are favorable. This transfer, otherwise known as conjugation, happens through sex pili. This differs from sexual reproduction because there are no gametes that fuse together, but this method does allow for genetic variation within a population.
This is how Plesiomonas shigelloides reproduces, now check out how it interacts with other organisms!