Classification:
How does Primula obconica relate to other organisms?
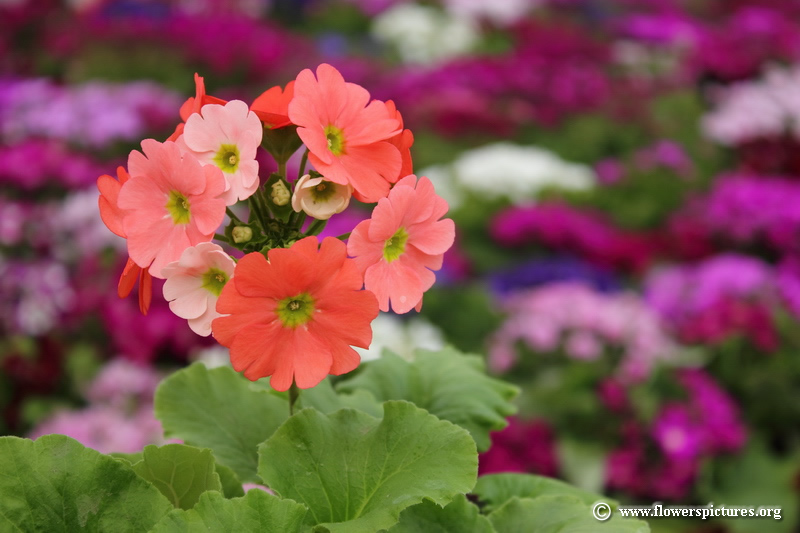 Domain : Eukarya
Domain : Eukarya
Kingdom : Plantae
Phylum : Anthophyta
Class : Dicotyledoneae
Order : Primulales
Family : Primulaceae
Genus : Primula
Species : Primula obconica
Common name: Poisonous Primrose
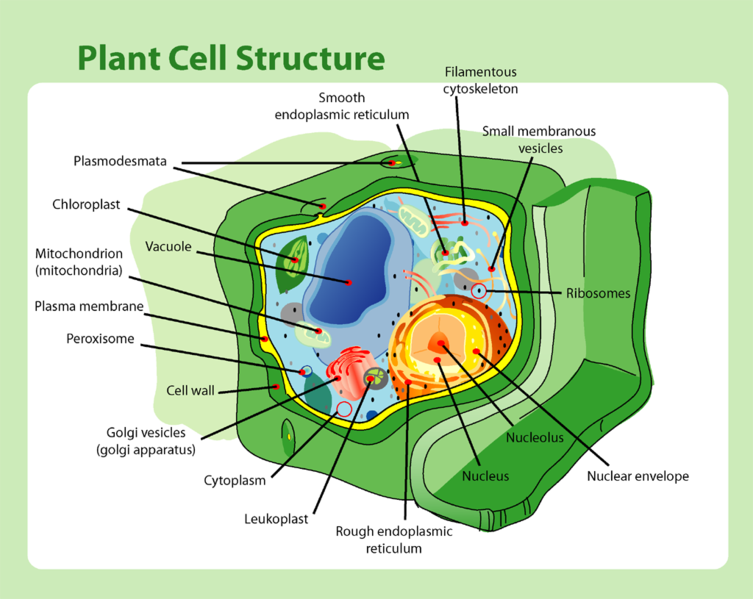
Primroses are classified as belonging to the Eukarya domain because its cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus that has genetic material. All organisms in this domain also have membrane-bound organelles. Mentha piperita (peppermint species) and Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Baker's yeast) are also Eukaryotes.
KINGDOM:
Primroses are under the kingdom Plantae because
it is a plant. Organisms in this kingdom have cell walls made of
cellulose, are
multicellular - less often unicellular or colonial, sessile
(non-motile), and undergo the process of photosynthesis except for a
few forms which have lost this ability. Photosynthesis allows plants
to use chloroplasts located inside their leaves to generate food
(Burns, 1974).
PHYLUM:
The phlyum Anthophyta classifies plants as flowering that have seeds enclosed within carpels which form fruits at maturity. The common name for plants in the Anthophyta plyum is angiosperm. Angiosperms are vascular which means that the Poisonous Primrose has the vascular tissues of xylem and phloem that are used to transport water and nutrients throughout the plant. Xylem and phloem allow vascular plants to grow larger in size than non-vascular plants. Other common features of this phylum include double fertilization and stamens with two pairs of pollen sacs (Burns, 1974).
CLASS:
The Poisonous Primrose belongs to the Dicotyledoneae
class. This class is commonly known as the dicots. A dicot contains
seeds with two embryonic leaves or cotyledons and all the other
features that are listed in Figure 1. Other members of this group
include
Salix alba (White Willow),
Toxicodendron raicans (Poison Ivy), and Passiflora edulis (Passion Fruit).
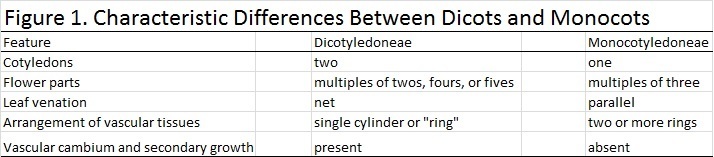
Figure 1 is a modified image from
The Plant
Kingdom.
ORDER:
Primulales is the order that encompasses the Poisonous Primrose. Members in this order are herbs or woody type plants with a well developed vestigial secretory system. Plants in this order often produce triterpenoid saponins. Some characteristics of this order include alternate leaves, flowers that are toothed or lobed, and fruits that are usually in a capsule, berry, or drupe. Primulales are dicotyledons with functional stamens and a compound ovary with a single style; this characteristic is only found in this group of organisms (Cronquest, 1981).
FAMILY:
The family Primulaceae includes the genera Primula, Anagallis, and Cyclamen. These genera are included in this family because they are distributed throughout the northern temperate climate. Plants in this family are usually herbs and have simple alternate or whorled leaves. The flowers are regular or in umbels. Members of Primulaceae have fruits that are in capsules (Burrows and Tyrl, 2001) (Frohne and Pfander, 2005).
"We are family, all my other genera and me"
GENUS:
Poisonous Primrose is a member of the Primula genus. It is classified in this group because it is a annual, it has leaves that form a basal rosette, and the capsules are globose or cylindrical. The toxicological importance of this genus is marked by the abundant occurrence of triterpenoid saponins present in the foliage because if ingested this toxin can cause negative effects on the digestive tract (Burrows and Tyrl, 2001) (Frohne and Pfander, 2005).
SPECIES:
Primula obconica, the Poisonous Primrose. Primula obconica has skin-irritant benzoquinone derivative in its secretory trichomes. It bears pink, lilac-blue, red, or white flowers. In Latin, primus or Primula means first and obconica means inversely conical (Frohne and Pfander, 2005).

Figure 2. How everything is related
Image from Offner, S. 2001. A universal phylogenetic tree. The
American Biology Teacher. 63: 164-171.
This tree represents how all the organisms in the universe are related and how they all originated from one origin of life. This tree is based on DNA structure. As you can see, plants are closely related to green algae which means they have similar DNA structure. For more information about green algae check out Spirogyra longata (filamentous green algae).
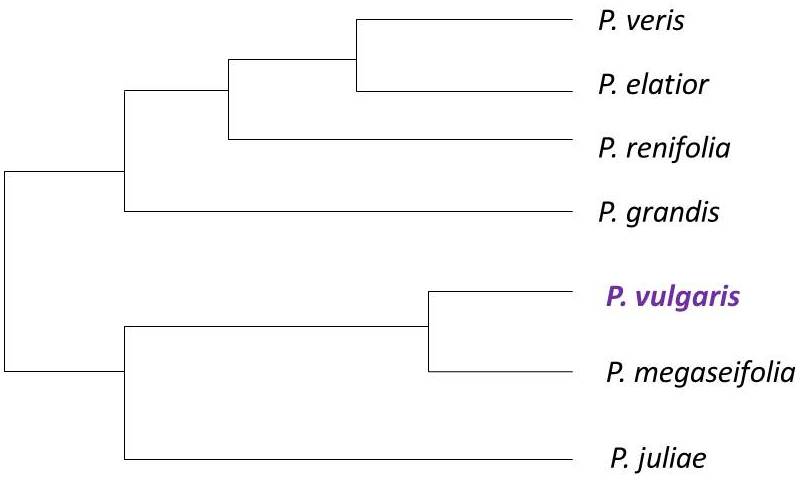
Figure 3. Closest relatives to the Poisonous
Primrose
This phylogenic tree is a modified image from the article "Phylogenetic
analysis of Primula section Primula reveals rampant non-monophyly
among morphologically distinct species." Click
here for citation.
The species above are also included in the Primula genus. This genus contains 500 species. The species in the tree are close relatives to Primula obconica. In a study, researches found that there are not many differences between the various species in this tree. However, the species did show non-monophyly to others in its section. Non-monophyly means that the taxon does not consist of a species and all its descendants. This tree is based on nuclear DNA sequences.
![]()
Where does this organism live? What does it call
home?
Click here to visit the habitat page.
Back to the home page.