Eastern Tiger Snake - Notechis scutatus
Friends & Enemies
Notechis scutatus are predacious reptiles that consume a variety of small warm-blooded mammals and birds, but they mostly feed on frogs. This helps control the population of the animals they consume. They are important contributors to the ecosystem because not only do they prey on others, but other predators prey on them for a source of food. As you know, eastern tiger snakes are not photosynthetic and this forces them to depend on other organisms to obtain energy and nutrients. They are secondary consumers and are located near the top of the food chain. The placement for this species within the food chain makes sense because they consume herbivores, or primary consumers, while being hunted at the same time by tertiary consumers. The main predators for the eastern tiger snake include bird and other snake species. The primary consumers, such as mouse, grasshopper, squirrel, or rabbit species, feed mostly on autotrophic producers that are able to generate their own food source and energy.
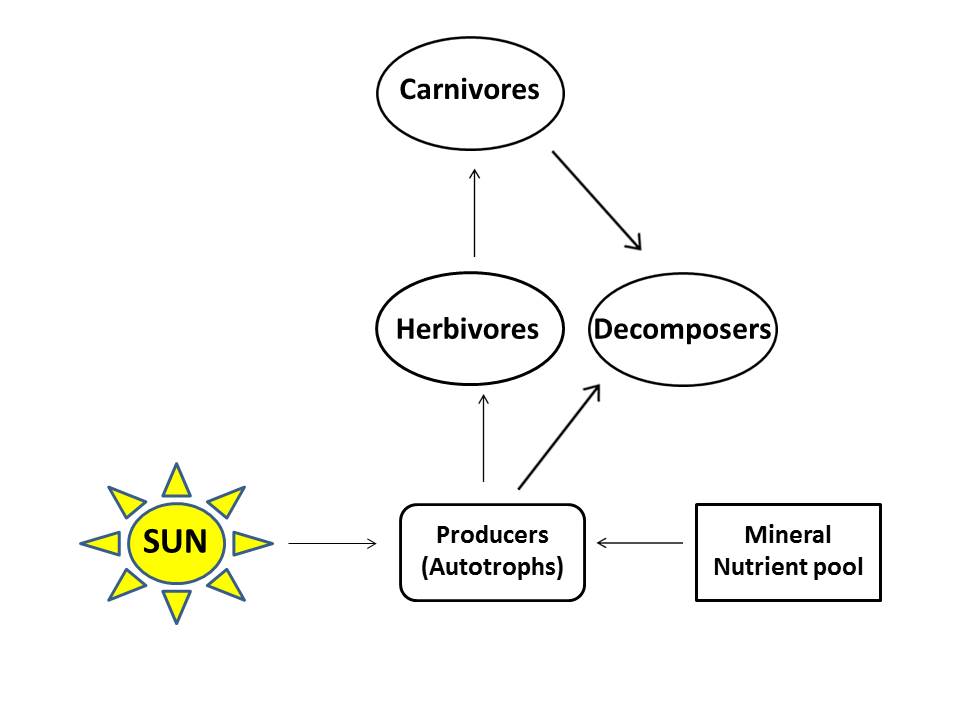
FIGURE: This is a modified illustration of the different levels within
the food web. Original image from Wikimedia Commons.
Due to the fact that the eastern tiger snake can live
in various habitats, they share their home with many other organisms.
From animal to plant to microbes, Australia is home to many organisms.
Some of the mammals found in the same habitats as Notechis scutatus
include the
Koala,
Water
Mouse,
Platypus,
Wallaby, and the
Flying-fox.
Accompanying the mammals, there are countless numbers of unique reptiles,
fish, insects, and bird species as well.
Although this specific tiger snake species does not
require a host, it does serve as a host for many parasitic animals.
Eastern tiger snakes are often hosts for members including
tapeworms,
ticks,
flukes, and roundworms.

Image used with permission of Tasmania Parks and Wildlife Service.
Next, learn about the components of the eastern tiger snake's special weapon or start from the home page again.