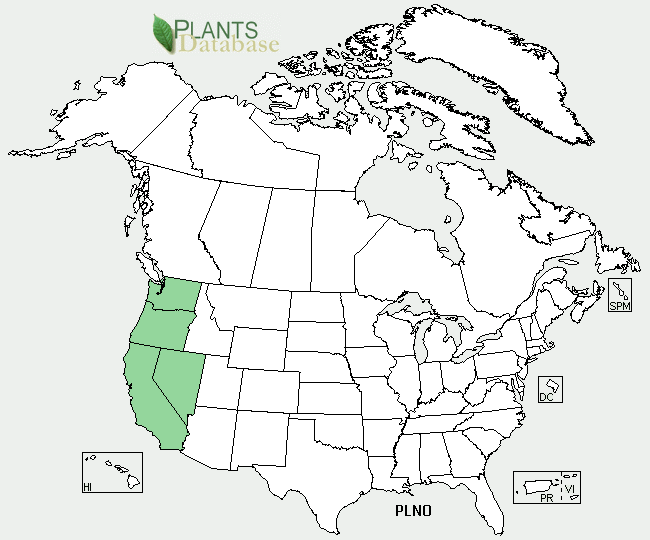
Where Can You Find Them?
Plagiobothrys nothofulvus
has a fairly restricted habitat. It is
found exclusively in the northwestern region of the United States,
mainly in northern California (Calflora 2014). It is native to
California (ITIS 2014). Populations of Plagiobothrys nothofulvus
have also been recorded in southern Washington state, specifically
in the Columbia River Gorge, and as far south as Baja California
(Rickett 1971).
The northwestern coast of the United States provides the ideal
growing conditions and climate for Plagiobothrys nothofulvus.
This region experiences a Mediterranean climate, with wet winters
and dry summers. It has been hypothesized that the long-term
weather patterns associated with this region of the United States
have led to a high level of biodiversity, thus allowing many
different species, including Plagiobothrys nothofulvus, to
develop (Lancaster and Kay 2013). As an annual herb, the main
blooming season for Plagiobothrys nothofulvus occurs from
roughly February- April, but it may be found blooming as late as May
(Calflora 2014, LBJ Wildflower Center 2014). During this time of the year,
California is in transition from its wet winter months to the
warmer, drier summers. It has been noted that roughly two-thirds of
the total annual precipitation in this region falls from December-
March, right in the middle of the blooming season for the popcorn
flower. Rainfall is much lighter from May- September, but the
region is never extremely dry (Talbot et. al 1939). The higher levels of
moisture at the beginning of the blooming season ensures that
Plagiobothrys nothofulvus is receiving enough water to grow
properly.
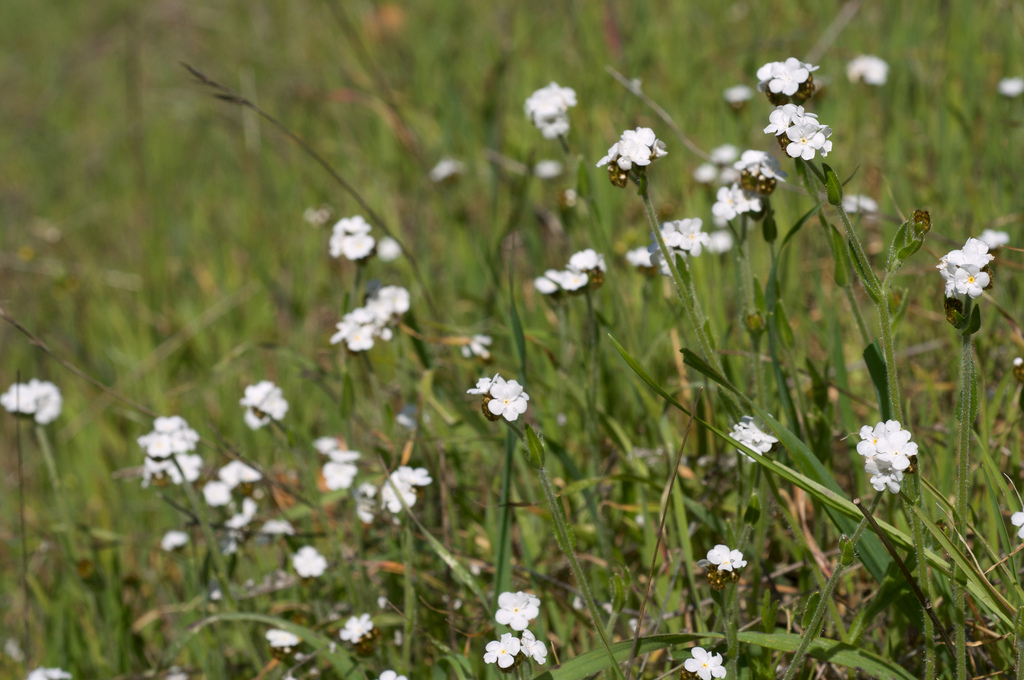
Popcorn flowers can be found growing in coastal grasslands, either
in flat fields or on the sides of hills (Talbot et. al 1939, Rickett
1971). These locations provide full sunlight, which is very
important to Plagiobothrys nothofulvus for photosynthetic
processes. Because of the great sunlight exposure in these areas,
popcorn flowers are usually found growing in fields with many other
types of plants. Some species that grow in habitats similar to or
with Plagiobothrys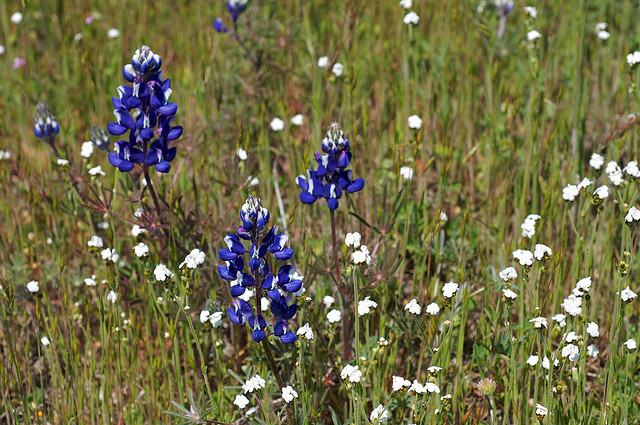 nothofulvus include Aster chilensis,
Lotus angustissimus, Plantago lanceolata, Galium
parisiense, and Brodiaea terrestris (Tierney and Cushman
2006). Other species that may be found growing alongside the
popcorn flower include
Elymus elymoides and
Bromus hordeaceus. All of these species require relative warmth and moist
growing conditions year round, so the Mediterranean climate of the
north and western United States is perfect for them. While
Plagiobothrys nothofulvus may be found growing among other
flowering plants, it is also commonly found in grass (LBJ Wildflower
Center
2014).
nothofulvus include Aster chilensis,
Lotus angustissimus, Plantago lanceolata, Galium
parisiense, and Brodiaea terrestris (Tierney and Cushman
2006). Other species that may be found growing alongside the
popcorn flower include
Elymus elymoides and
Bromus hordeaceus. All of these species require relative warmth and moist
growing conditions year round, so the Mediterranean climate of the
north and western United States is perfect for them. While
Plagiobothrys nothofulvus may be found growing among other
flowering plants, it is also commonly found in grass (LBJ Wildflower
Center
2014).