How would you classify this species?
North-west Italian Cave Salamander, French Cave Salamander,
and Strinati’s Cave Salamander are all the common names
referring to the species, Speleomantes strinatii (IUCN Red List
of Threaten Species 2014; Reptiles & amplibiens de France
2004). The genus name for
this species has two meanings. The first part of Speleomantes
means “cave,” and the second part, “mantes” comes from the god
from hell, Mantus (Reptiles & amplibiens de France 2004).
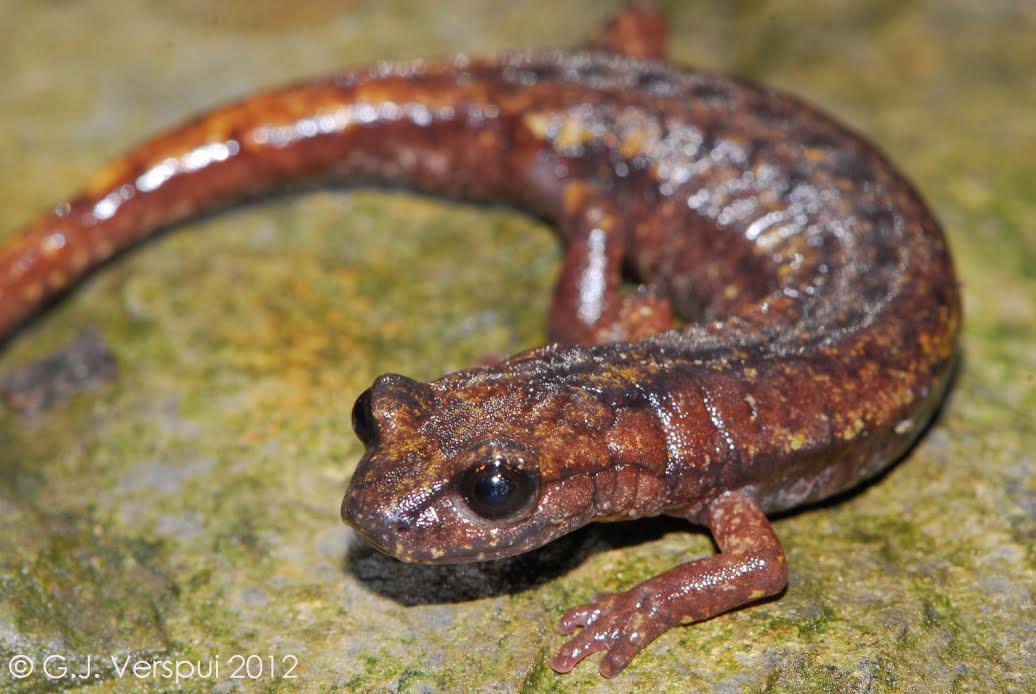
Photographed by
Gert
Jan Verspui in April 2012
in Liguria, Italy. This is a photo of Speleomantes
strinatii.

Classification:
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Amphibia
Order: Caudata
Family: Plethodontidae
Genus: Speleomantes
Species: strinatii
(IUCN Red List
of Threatened Species 2014).
Why is the North-west Italian Cave Salamander classified in these categories?
Domain: Eukarya
All organisms in this domain have a true nucleus.
These organisms can range from unicellular to multicellular
(Campbell et al. 2008). The
Sweet Potato, the
Cranberry, and the
Mute Swan are also in this domain. There are informative
websites on all of these organisms from the database,
MultipleOrganisms.net.
Kingdom: Animalia
All animals are considered to be multicellular. They are all
heterotrophic eukaryotes. Every animal has tissues that develop to
form embryonic layers. Animals can be classified further with
specific synapomorphic traits such as, body plan symmetry,
organization of tissues and protostome verse deuterostome
development (Campbell et al. 2008).
MultipleOrganisms.net has many informative websites on species
in this same kingdom such as the
American Alligator, the
Red Rock Crab, and the
Giant Pacific Octopus.
Phylum: Chordata
All chordates have a notochord, a dorsal hollow nerve
cord, pharyngeal slits and a muscular postanal tail (Campbell et
al. 2008). All chordates
are also bilaterally symmetrical (Campbell et al. 2008).
Also in this phylum are the
Timber Rattlesnake and the
American Bullfrog.
Class: Amphibia
There are three major clades that consist among living amphibians.
These clades are caecilians, salamanders and frogs (Zug et
al. 2001). Among the Amphibia, there are only around 550
species of urodeles. Most land living salamanders walk with a
side-to-side motion while bending their bodies. This trait was
inherited by early tetrapods living in terrestrial environments
(Campbell et al. 2008).
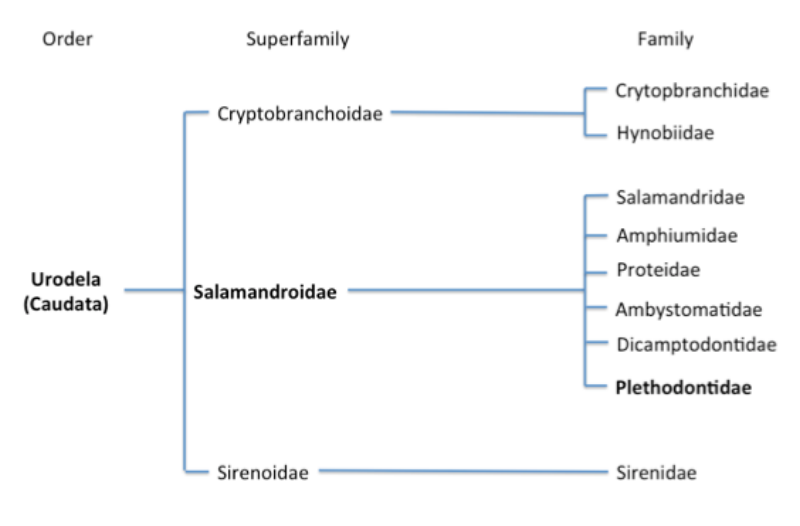
Order: Caudata
Salamanders are labeled with a node based name, Caudata.
This means the organism has a tail. It is common for these organisms to have cylindrical bodies,
long tails and well developed limbs. Some salamanders have
limbs that a greatly reduced or even lack hind limbs. Salamanders,
in general, can live in many different places such as aquatic
environments, terrestrial environments, and forest canopies (Zug
et al. 2001).
Family: Plethodontidae
Genus:
Speleomantes
Speleomantes strinatii is one of the seven species in the genus, Speleomantes (Carranza et al. 2007). Species in this genus can be found in southeastern France, northern and central Italy, and Sardinia, a Mediterranean island (Carranza et al. 2007).
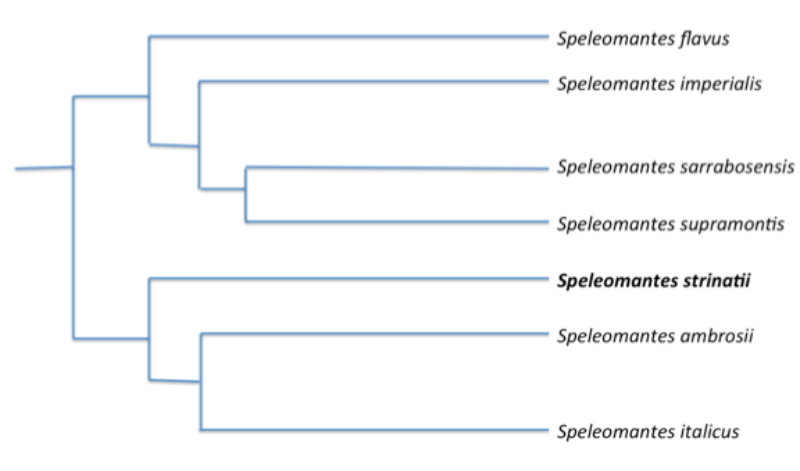
Figure 2. Phylogenic tree including the
seven species in the genus, Speleomantes (Carranza et al.
2007). The scientific name for the North-west Italian Cave
Salamander is bolded. Modified by Mary Purdy.
There are only seven cave salamanders
documented that are living in Europe. These species all share a
common ancestor from the genus, Hydromantes, which is located in
California (Carranza et al. 2007).
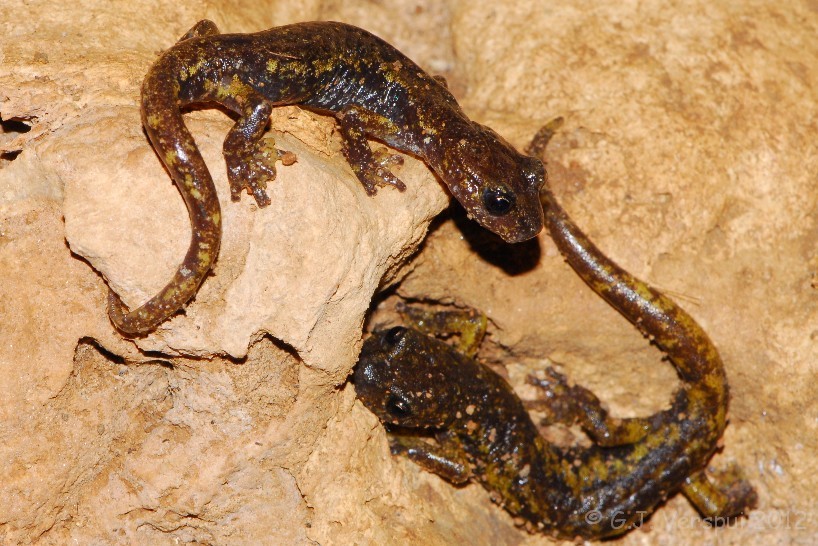

Photographed by
Gert Jan
Verspui in April 2012 in Liguria, Italy. This is a photo
of
two Speleomantes italicus. If you
would like to look at more pictures of organisms in the genus, Speleomantes,
or other
amphibians, you can visit Gert Jan Verspui's Website
here.
Species:
strinatii
This species was dedicated to Pierre Strinati,
hence the name of the species (Reptiles
& amplibiens de France 2004).
Interested in learning more? Read
about where in the world Speleomantes strinatii
lives!
Return to Home Page.