|
Current Level |
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
Previous Level |
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
PROTEIN FAMILIES
Primary Structure (amino acid sequence) Motifs (sequence) Secondary Structure (alpha helix and beta sheet) Motifs (structural) Domains Tertiary Structure (overall 3-D structure)
MOTIFS Motifs are conserved primary sequences or simple combinations of a few secondary structural elements. Motifs (sequence) Glycosylation sites, phosphorylation sites, ATP binding site
Motifs (structural) Helix-turn-helix (H-T-H): 2 alpha helices Zn finger: alpha helix and beta sheet Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF)
DOMAINS Domains are fundamental units of tertiary structure. These are polypeptide chains that can fold independently into a stable tertiary structure. They can also form units of function. Domains are built from structural motifs.
Transcription Factors (TF) - bind to DNA and turn genes on or off.
Helix-turn-helix motif DNA binding domains (H-T-H) Dimerization domains (alpha helix)
PROTEIN FAMILY By swapping domains a proteins activity can be changed New proteins are made by exchange of domains and by mutations within domains Add additional domains or make mutations to change members of the same family.
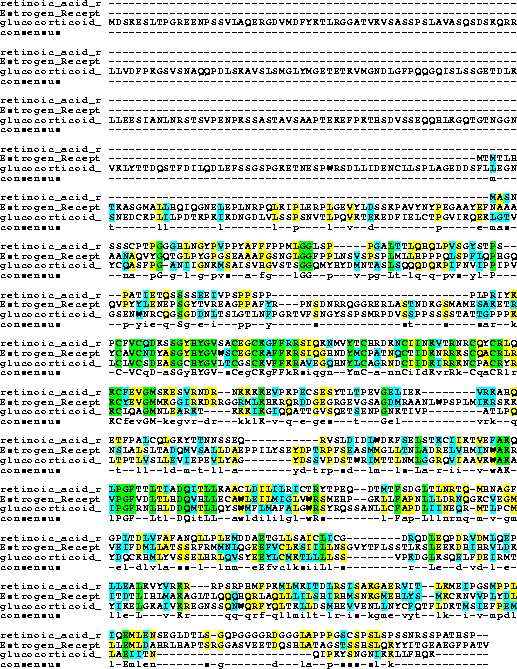
Glucocorticoid receptors - similar structure with different DNA binding and hormone binding domains
Motif Search Look at DNA binding motif in steroid receptors
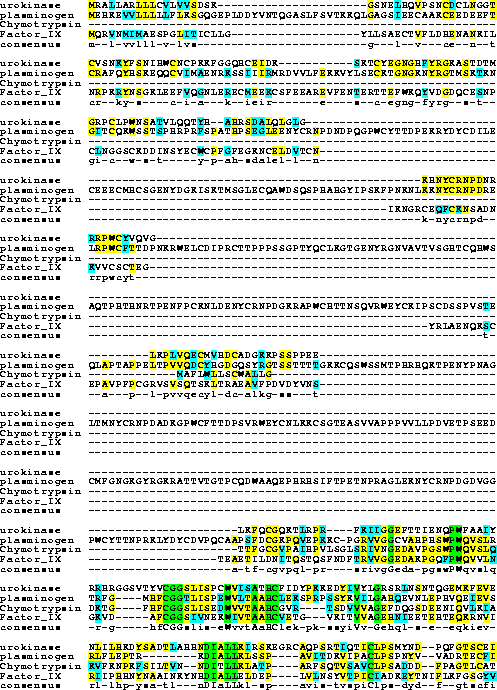
Serine Proteases
Urokinase Factor IXPlasminogen
Motif Search Compare Urokinase, Factor IX and Plasminogen
|
|
|
|