|
Current Level |
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Previous Level |
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
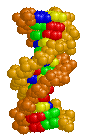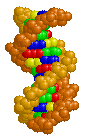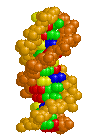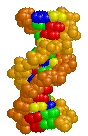
| DNA Structure |
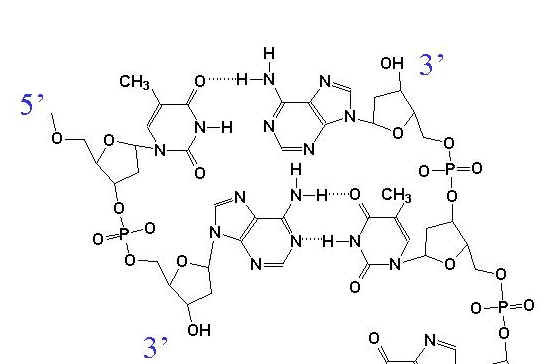
BackgroundDNA is composed of two antiparallel strands of deoxynucleotides held together by hydrogen bonds between purine (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidine (thymidine and cytosine) bases. This structure was solved from X-ray crystallography data and presented by J. D. WATSON and F. H. C. CRICK A Structure for DNA (Nature April 2, 1953). The 1962 Nobel Prize in Medicine was also awarded for this work.
Backbone ComponentsRNA (ribonucleic acid) is made up of ribose sugars attached to each other through phosphodiester bonds. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is made up of deoxyribose sugars attached to each other through phosphodiester bonds.
The phosphodiester bond forms between the 5' OH group on one sugar and the 3' OH group on the next sugar in the chain.
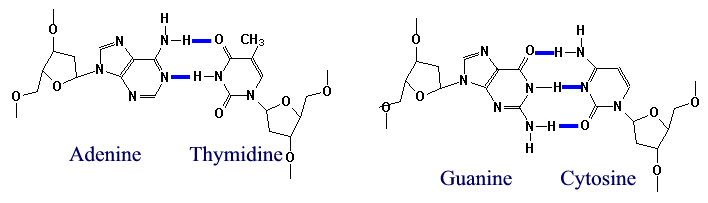
Hydrogen BondingHydrogen bonds form between a hydrogen donor (O-H, N-H) and an hydrogen acceptor with free pair of electrons (O:, N:). As a result, Adenine-Thymidine base pairs form two hydrogen bonds and Guanine-Cytosine base pairs form three hydrogen bonds. Major Groove
Major and Minor GrooveThe alignment of the deoxyribose sugar groups on each nucleotide are not symmetrical around the center of the axis. This results in the formation of a major groove and a minor groove in the DNA molecule.
Practice Problems
|
|


 Minor Groove
Minor Groove