|
Current Level |
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Previous Level |
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Forensics |
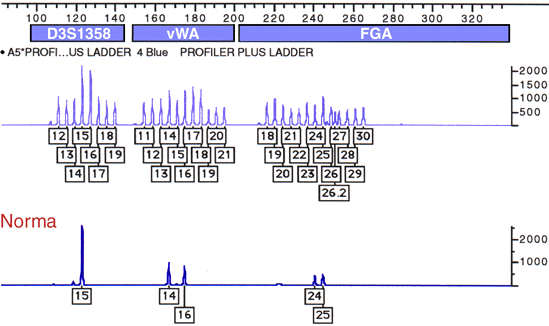
Short Tandem Repeats (STR) are made up of relatively short DNA sequences that are repeated in tandem. STRs form by unequal crossing-over during meiosis. This results in a large variety in the numbers of repeats in a population.
To determine which alleles of an STR a person has in their two chromosomes, PCR primers are designed that flank the STR region. The PCR products are then run on a gel or capillary system to separate them by size. By looking at multiple different STR regions throughout the genome, a specific pattern of PCR products emerges for each individual.
The FBI uses thirteen core loci for the Combined DNA Index System (CODIS) database. By standardizing the system, samples collected around the world can be compared.Calculating Probabilities of a Match You can multiply the probability of having each genotype to find the probability of having a match at all 13 sites by random chance. The program below will do the calculations for you. As you can see, the probabilities are very low. http://www.csfs.ca/pplus/profiler.htm
Some very useful educational links on the use of DNA in forensics:http://www.blc.arizona.edu/courses/181gh/rick/DNA_profile/intro.html http://www.cstl.nist.gov/biotech/strbase/multiplx.htm http://www.biology.arizona.edu/human_bio/activities/blackett2/overview.html http://www.fbi.gov/hq/lab/codis/index1.htm http://www.ornl.gov/TechResources/Human_Genome/elsi/forensics.html
|
|