Classification
|
Domain: Eukarya |
Eukaryotic because
Dipylidium caninum possesses
a true nucleus and membrane
bound organelles. |
|
Kingdom: Animalia |
|
|
Phylum: Platyhelminthes |
Because Dipylidium caninum is an invertebrate with an unsegmented body and bilateral symmetry without a body cavity, it is in the phylum platyhelminthes. |
|
Class: Cestoda |
Being a parasitic flatworm that
lives in the digestive tract of
vertebrates, Dipylidium caninum is found in the class of Cestoda. |
|
Order: Cyclophyllidea |
In the order cyclophyllidea, all the organisms including Dipylidium caninum are parasitic in domestic animals and have four suckers on their scolex, and multiple proglottids. |
|
Family: Dipylidiidae |
Unlike other cyclophyllidea, the family dipylidiidae taking account of Dipylidium caninum have genital openings on both sides of the proglottids instead of just one side. |
|
Genus:
Dipylidium |
All the combined traits above and this organism occupys the intestines of domesticated animals. |
|
Species: Dipylidium caninum |
|
Below is a cladistic phylogenetic tree of the Eukarya domain. Here
it shows us classification of all the organisms that possess a true
nucleus. Specifically you can follow the blue highlighted route and
see the platyhelminthes relation to other organisms. This tree
visually shows us how closely related each organism is to another.
The relations in this particular tree are dependent on
organisms' DNA
sequences. In other words,
how different genes relate to other organisms.
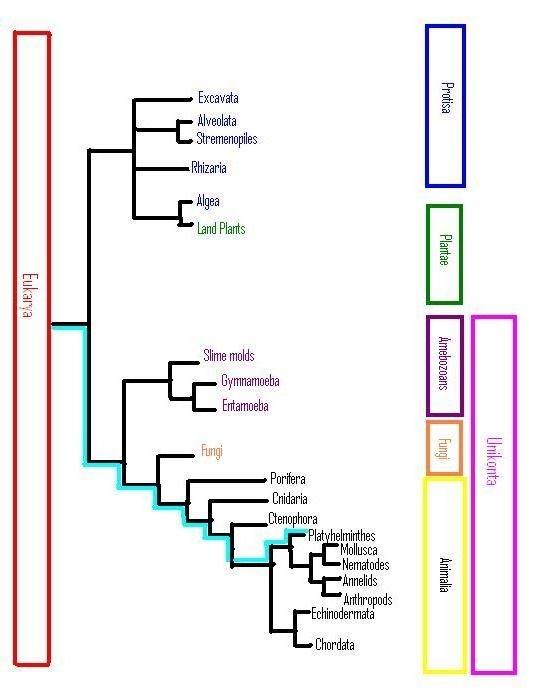
Here you can
see and explore another organism in the platyhelminthes phylum.
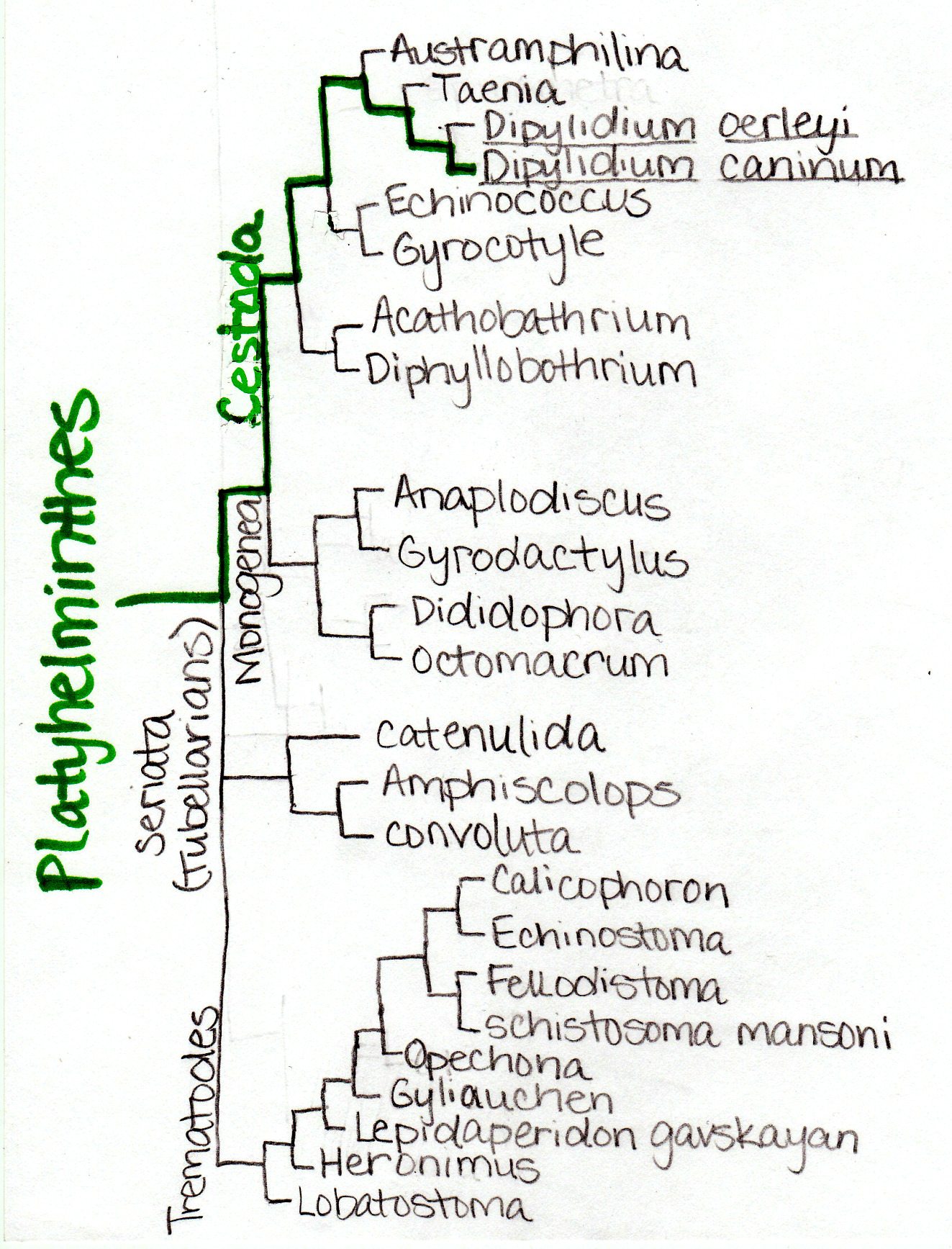
This
cladistic phylogenetic tree takes a closer more specific
look at the phylum platyhelminthes. Again, the relations
you see here in this tree are based on genetic DNA genes
and sequences.
B