Six Feet Under
Streptomyces griseus has a large environmental role as a decomposer and overall production of certain bioactive metabolites (many which are natural antibiotics) which are used extensively in medicine to fend off disease.
 Antibiotics,
many which are derived from this category of bacteria.
(Provided by Oregon Health)
Antibiotics,
many which are derived from this category of bacteria.
(Provided by Oregon Health)
The antibiotics derived from Streptomyces
griseus will be discussed later on, as they're some of the most
important today. To get back on track Streptomyces griseus lives
mostly in soils across the world, along with some researchers have found it
in beaches and other sediments. This habitat has the potential for many
different organisms and contains thousands if not millions of other species
of bacteria.
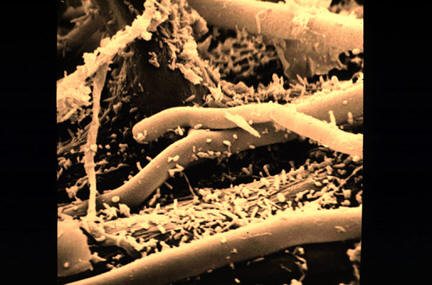 Fungal
hyphae in soil with many bacteria clinging to them. (Provided by The
United States Department of Agriculture)
Fungal
hyphae in soil with many bacteria clinging to them. (Provided by The
United States Department of Agriculture)
This
bacteria is successful in its soil environment as it works in a lot of the
same way that a fungus does, in that it breaks down material, creating
richer soil for future farmers. And with having a very complex life cycle
and structure this bacteria can grow quickly and survive in even fairly
acidic environments, which since soil is generally alkaline in nature, is
impressive.
With this large amount of organisms in an area Streptomyces
griseus has adapted a way of life very similar to that of the fungi in
terms of how this organism gets its nutrition and even its internal
structure. This leads into the movement of this bacteria, which as you can
imagine from what I just stated, is almost exactly the same as a fungus. Streptomyces
griseus moves by using exoenzymes of all kinds, due to a large genome
that allows the bacteria to respond to its environment and secrete the
enzymes needed to digest the material around it. Overall, the functions and
underlying importance of structure will be covered in the next section as we
delve into the key as to how this organism flourishes in its environment.
Next, how Streptomyces griseus thrives in
its environment and the overall life cycle of this bacteria: