Classification
All organisms are classified into groups from most to least inclusive. The Fox Grape is put into the categories it is in because of the characteristics it has, and more recently because of DNA differences and similarities with other organisms.
Domain: Eukarya
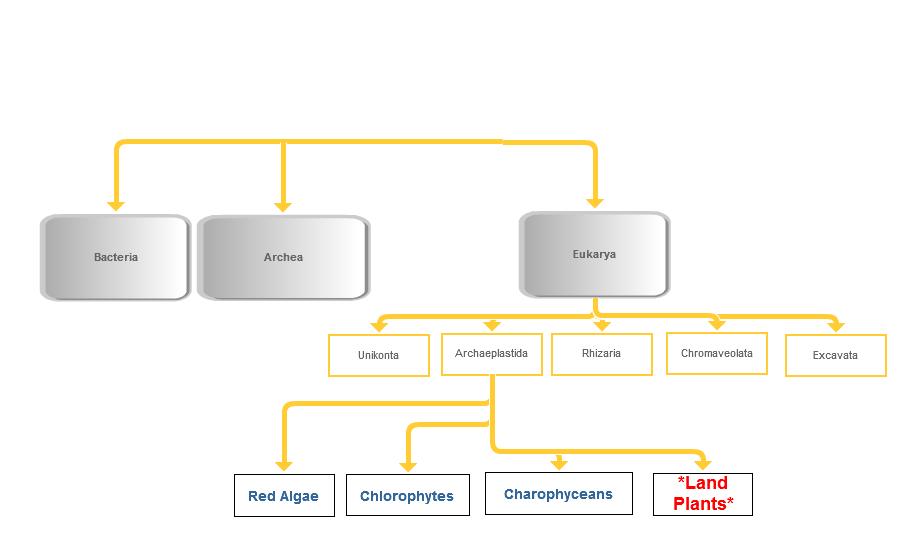
Vitis labrusca is in the domain Eukarya. Some characteristics that place the Fox Grape in this domain are: multicellularity, a nucleus and other membrane bound organelles, and multiple chromosomes. This is compared to the domains Bacteria and Archea where most of them are unicellular with no membrane-bound organelles and a single, circular chromosome. Under this broadest form of classification, Vitis labrusca is related to organisms like Dipylidium caninum (a tapeworm) and Panthera uncia (Snow Lepoard).
Kingdom: Plantae
The Fox Grape is placed in the kingdom plantae because, well, it's a plant! Some of the general characteristics that make Vitis labrusca a plant are: they are multicellular, have the ability to photosynthesize, and have a cell wall made up of cellulose. Other examples of plants are: Triticum aestivum (Common Wheat) and Achillea millefolium (Yarrow).
Subkingdom: Tracheobionta
The Tracheobionta subkingdom is where all of the vascular plants are. Vitis labrusca is part of this group because it has specialized tube-like structures that transport nutrients and water throughout the plant. It is because of the ability to transport that vascular plants have been able to grow bigger and taller than the nonvascular plants that depend on diffusion to get what they need. Under this category, Vitis labrusca can be grouped with plants like Polypodium glycyrrhiza (Licorice Fern) and Pinus strobus (Eastern White Pine).
Superdivision: Spermatophyta
The Spermatophyta are the seed plants. In plants with seeds, the ovule (female) is encased in a hard outer covering and the pollen (male) gets distributed by many different means. Other examples of seed pants are: Swietenia mahagoni (West Indies Mahagony) and Viola sororia (Common Blue Violet).
Phylum: Anthophyta
Vitis labrusca belongs to the phylum Anthophyta (angiosperm) which means it is a flowering plant. The flower is the location for sexual reproduction in these plants. Flowering plants are also the ones that produce fruit. The fruit is an enlarged mature ovary. Other plants included in the phylum Anthophyta are Dioscorea villosa (Wild Yam) and Cynara scolymus (Globe Artichoke).
Class: Magnoliopsida
This class is more commonly known as the dicots. Characeristics that VItis labrusca has that makes it a dicot are: net-like leaf veins, secondary growth (has a woody stem), two cotelydons and flower parts in groups of 4 or 5. Citrus sinensis (Sweet Orange) and Toxicodendron radicans (Poison Ivy) are other examples of dicots.
Order: Rhamnales
The families in the order Rhamnales have DNA similarities that put them in one category. Before the ability to analyze DNA, many of the families put in Rhamnales were not considered to go together.
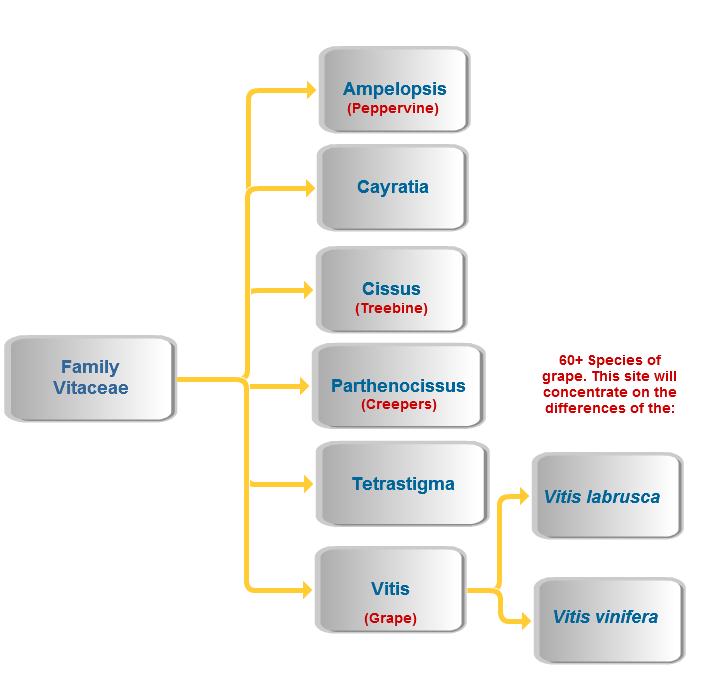
Family: Vitaceae
Vitaceae are the grapevines and the vine shrubs that are related to grapes.
Genus: Vitis
Specifically the grapevines
Species: Vitis labrusca
A north American grapevine species known for its "foxy" aroma and slip skin.

