Classification
DOMAIN: Eukaryote
Cells contain complex organelles located inside their membranes.
KINGDOM: Plantae
The ghost chili is a photosynthetic organism that undergoes an alternation of generations lifecycle.
PHYLUM: Angiosperm
This organism is a flowering plant in which its seeds develop within the flower's ovary and eventually form the fruit.
CLASS: Eudicot
Besides being vascular, there are two main characteristics that categorize eudicots, and the Bhut jolokia has both of them. First, the flowers on the chili plant contain five pedals, and second, its veins located on the leaves are net-like.
ORDER: Solanales
Located on the stems of this chili plant, there are small branched hairs.
FAMILY: Solanaceae
The ghost chili fits into this family because with in its fruits, there are many seeds that are contained within a capsule. The leaves on this plant are alternate and mostly unequal pairs. The flowers on these plants are usually "perfect", meaning that they all have both sexes present. Other organism in this family include tomatoes, eggplants, tobacco, and potatoes.
GENUS: Capsicum
Because the ghost chili can produce capsaicin, it belongs in this genus. The only organism that does not produce capsaicin with in this genus is the sweet tasting bell pepper.
SPECIES:Interspecific Hybrid Between C. chinese and C. frutescens (Bhut Jolokia)
This species is a naturally occurring interspecific hybrid between two species in the Capsicum genus. For the most part this chili is more closely related to the C. chinese, but it has inherited the long thin chili shape that the C. frutescens possesses. Scientifically the ghost chili is called the Bhut jolokia. The word bhut is from Indian origin, and literally means sprit or demon. Jolokia, another word with Indian origin, is just a different word that describes chilies within the Capsicum genus.
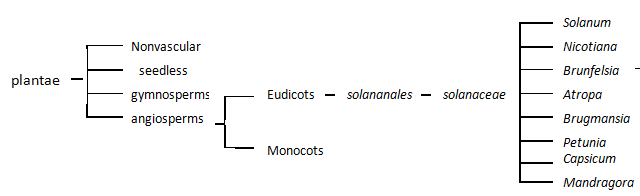
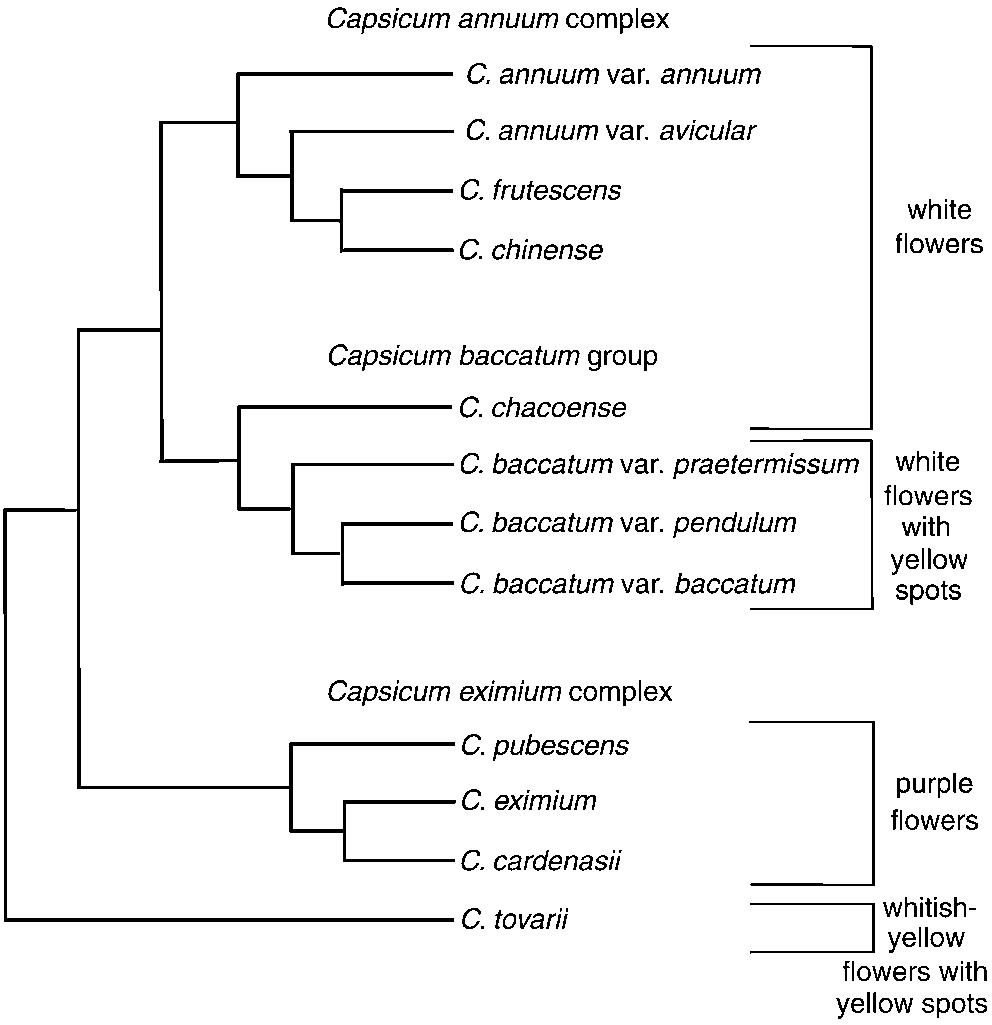
Phylogenetic Trees:
Below are two cladistic phylogenetic trees that represents where the Bhut jolokia fits within the grand scheme of classification.
The first phylogenetic tree, above, represents where the genus Capsicum lies compared to other organisms. This is a broad tree that depicts categories from family to genus. The data used to make this tree was based off of morphological features that all of these organisms share. The ghost chili is a close relative with the tomato (Solanum), tobacco (Nicotiana), and potatoes.
Above is another phylogenetic tree that displays how the genus Capsicum is differentiated. This information is based off of the different flower colors present in the genera. Because the Bhut jolokia is an interspecific hybrid, it belongs in between the C.frutescens and the C.chinese, and possesses white flowers. This tree also shows that C.chinese and C.frutescens share a common ancestor with each other.