Classification
Domain: Eukarya

Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum:
Chordata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Chiroptera
Family: Phyllostomidae
Genus: Desmodus
Species: Desmodus rotundus
Desmodus rotundus is a Eukarya. Eukarya refers to a group of organisms that have cells deemed "eukatyotic". Eukaryotic cells are those that posses membrane bound organelles and true nuclei. Eukaryotic cells are also capable of cell division via mitosis.
Animalia
All members of the Kingdom Animalia are heterotrophs. Heterotrophs are those that rely directly or indirectly on others for food. Members of the Animalia kingdom are also multicellular. Desmodus rotundus is also mobile just as every animal is at some point in their life.
Chordata
Those classified as Chordata all possess a notochord at some
point in their life. Chordates also possess a post anal tail in one
or more stages of their life cycle.
Mammalia
Synapomorphies (shared traits) for the class Mammalia include hair or fur
covering the body, respiration through lungs, production of milk
for their young via mammary glands and the need to maintain a
constant body temperature in order to survive. To read more about
the specific reproduction methods of Desmodus rotundus
check out the reproduction page.
A characteristic of Chiroptera is flight. Bats, being the only mammals that have the ability to fly, compose the order chiroptera. The word chiroptera is of greek origin, chiro- meaning hand and -ptera meaning wing.
Phyllostomidae
Phyllostomidae is a family containing tropical and
subtropical bats. Members of this family are broad winged and have a
simple spear- shaped body plan. A long with a shared body shape is
the presence of a nose leaf (britannica.com). Also, the bats that
contribute to this family prefer to live in groups that often range
in size.
Desmodus
The
common vampire bat is the only member of this specific genus.
According to the Merriam Webster Latin Dictionary, the
word Desmodus breaks down into a literal meaning of "two
thirds way" Des meaning two thirds and modus meaning way.
The full species
name for the common vampire bat is Desmodus rotundus. The
meaning of the Latin word rotundus is round or spherical. When
combing the genus and species name Desmodus rotundus
translates to "two thirds of the way round." This is more than
likely in reference to the bat's unique body shape.
Phylogenies
I
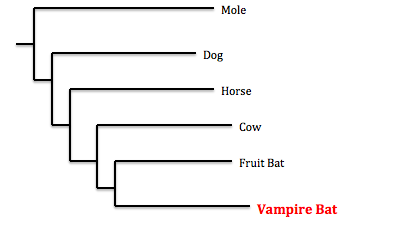 rodents.
Even thought the vampire bat resembles a sort of flying rodent, molecular data, found by tracing the TRPV1 locus in mammals, proves that bats are actually more closely related to
cows and horses than they are to rodents (Racheva et al. 2011).
rodents.
Even thought the vampire bat resembles a sort of flying rodent, molecular data, found by tracing the TRPV1 locus in mammals, proves that bats are actually more closely related to
cows and horses than they are to rodents (Racheva et al. 2011).
<
Learn more about the habitat of the common vampire bat here!