Interaction with other species
Interaction with cats
A few fleas on adult dogs or cats cause little harm unless the
host becomes
allergic
to substances in saliva. The disease that results is called
flea allergy dermatitis.
Small animals with large infestations can lose enough blood to
fleas feeding that
anemia
may result. Fleas are also responsible for disease transmission.
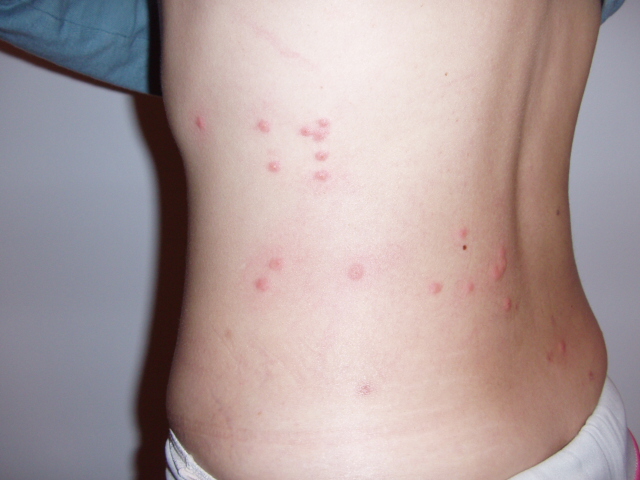
Cat fleas on domestic pet can hoop onto human. The parasites on flea can thus pass to human. The most common problems includes flea allergy dermatitis (FAD), tapeworms, secondary skin irritations and, in extreme cases, anemia.
Although bites may be rarely felt, it is the resulting irritation caused by the flea salivary secretions. If one has reaction to the saliva, red itching spots may occur. There is usually single point at the center of the spot.
Tapeworms normally infest dogs and cats but may appear in children if parts of infested fleas are accidentally consumed.
When female cat flea meet a male cat flea, love might occur between them. If there is strong attraction holding the two together, copulation occur.
Bacteria in fleas gut
Rickettsia can be found in gut of fleas. They are carried as parasites by fleas and can cause diseases such as typhus, rickettsialpox, Boutonneuse fever, African Tick Bite Fever, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, Australian Tick Typhus, Flinders Island Spotted Fever and Queensland Tick Typhus in human beings.
← Life cycle Reference →