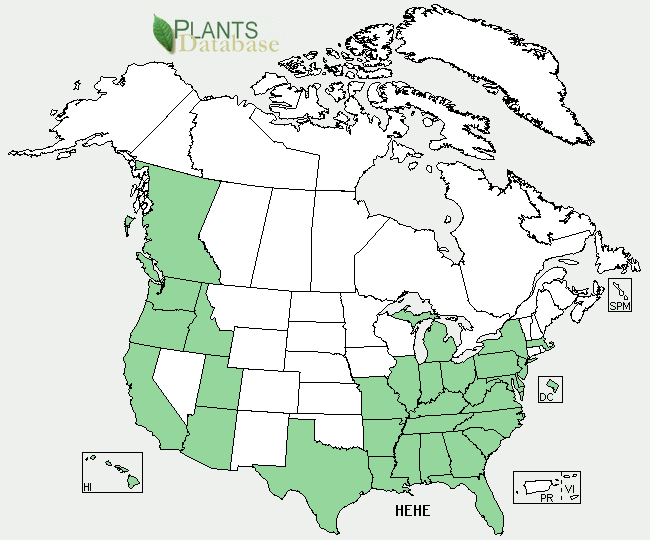
Habitat
English Ivy is native to Europe and Western Asia. Areas that this plant occupies include deciduous forest edges, woodlands, hedgerows, coastal areas, salt marsh edges, and other upland areas. These areas have just the right soil type for English Ivy: wet, but not extremely wet.
Most garden soils are adequate for Hedera
Helix, along with many other types. This plant likes
its soil to be well-drained and moist, but it is
far from picky.
As long as the soil is not
 extremely
wet, English Ivy will survive. Some can survive in full
sun and deep shade, but what the ivy really prefers is slightly
sunny to shady light. It does the best in the winter sun
and summer shade and prefers the cold and
heat tolerant zones of
4-9.
extremely
wet, English Ivy will survive. Some can survive in full
sun and deep shade, but what the ivy really prefers is slightly
sunny to shady light. It does the best in the winter sun
and summer shade and prefers the cold and
heat tolerant zones of
4-9.
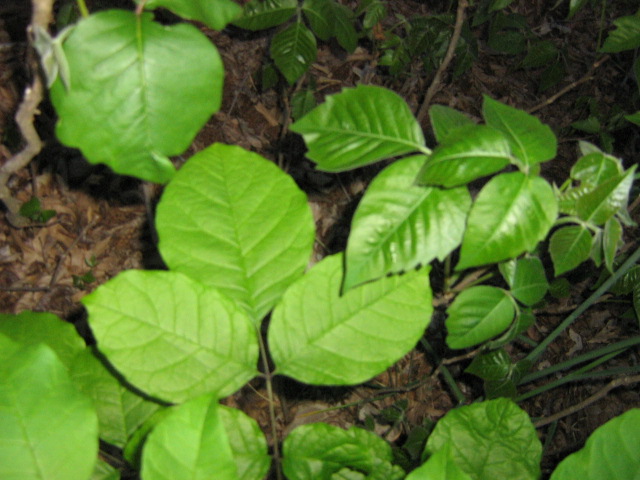
In its habitat, English Ivy is usually surrounded by larger organisms that it can crawl up. Most common neighbors to the plant are deciduous trees, such as elms, oaks, and maples. Sometimes they live near evergreen pine trees, and they are often seen around fellow ivy plant Poison Ivy. A lot of times, it is difficult to distinguish between the English Ivy and the Poison Ivy.
Poison Ivy Leaves English Ivy Leaves