



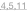






Figure 2. outlines the phylogeny of the genus Solanum and shows the close relationships of the cousins to the tomato, which include potatoes, tobacco, chili peppers, and aubergine. The closer the species is to the tomato represents the how many characteristics are shared. For example, the tomato and the potato are derived from a very close ancestor, showing they are very similar species. Whereas coffee and tomato only share a very distant ancestor, which allows for further adaptations and mutations in each species. Figure 2 is based on the morphological characteristics of the species listed.
Figure 2. Close Relatives of the Tomato

Classification:
In the kingdom of plants, the tomato is part of the angiosperms, with the fruit being the tomato. As a eudicot, the leaves have net-like veins with floral organs in multiples of four or five. It is further classified into the order solanales and is part of the Solanaceae or nightshade family, which refers to the dark colored poisonous berries of other organisms in this family. A summary of the classification of the tomato is found in Figure 1.

Check out these other organisms that are closely related to the tomato!
Prunus cerasus (sour cherry)
Site designed by Chloe Scheel, Last updated April 2009.












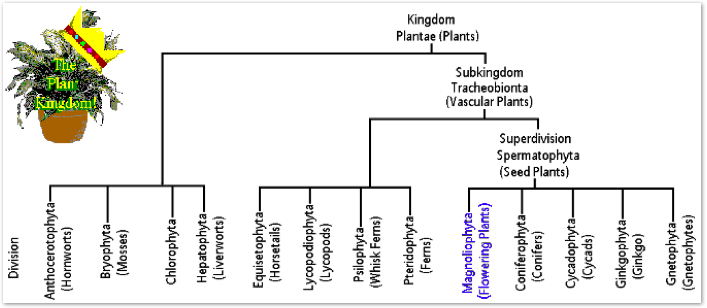
Seeing how the tomato is classified within the genus Solanum, Figure 3 traces the tomato back the Kingdom Plantae. As seen in Figure 3, the phylogenetic tree is broken down by physical features of each plant.

Figure 3. Taxonomic Tree of the Plant Kingdom.
The tomato did not originate in the United States. Ever wonder how it made it to U.S.? Or even here in La Crosse, Wisconsin? Check out the history of the tomato!
