Characteristics
The Original Soybean
The original soybean plant was wild. It was an annual green vine with small and narrow leaves that had a grouping of three leaves. It bore very small purple flowers, and small, hard, roundish black to dark brown seeds. These seeds were brittle at maturity and could shatter easily.
Today's Soybean
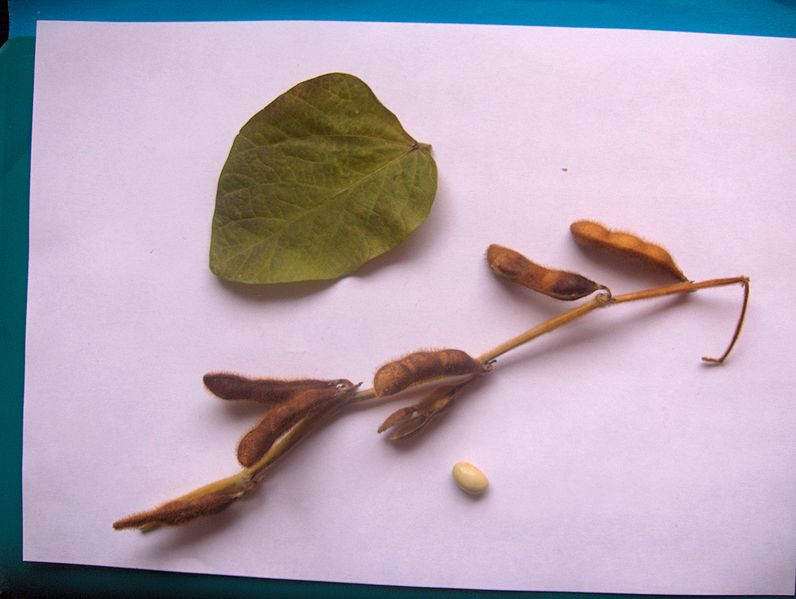
Today domesticated soybean plants are annuals that consist of tall upright bushes. They have leaves, pods, and stems that are typically covered with soft brown hairs. Plants have trifoliate leaves with netlike veins and a branched tap root. Blooming, pod formation and maturation are specific stages of development, and as maturity approaches, the leaves turn yellow and usually drop off before the pods mature.
Flowers are small, white or purple, borne on short stems rising from stem nodes, and flowering proceeds rapidly from base to tip. Flowers develop into pods, which are small, straight or slightly curved, covered with hair, and contain one to four seeds. These seeds differ with variety (from round to elliptical), and in color (from straw yellow to various shades of green, brown or black).
Seeds are found in a seed coat which protects the seed from damage and drying out as it matures. Soybean seeds are an important source of oil and protein.
Soybeans are ready to harvest when seeds turn hard, or as soon as its leaves fall. Harvest is usually delayed until seeds are well dried on its standing stalk. Mechanical harvesting is usually done by combines, as you can see in this picture.
Reproduction
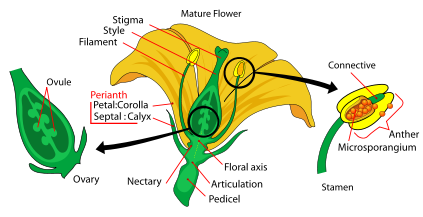
Soybeans reproduce through alternation of generations. This term means that there times in the life cycle when haploid and diploid phases are seen. Soybeans also have male and female parts. ♀The female part of the soybean plant is called the pistil, which includes the style, stigma, and the ovary. ♂The male part is called the stamen, which includes the filament and anthers. Anthers contain the pollen.
Soybeans are mainly self-pollinated. This means that pollen (remember, male part) from the same plant fertilizes the ovary (female part). Fertilization may be caused by bees (Apis mellifera) and other insects, which is known as natural fertilization. This natural fertilization occurs when insects travel to flower petals to drink nectar. While in the flower, insects unknowingly rub against the pollen, which sticks to various parts of the insect. It then moves on its way to another flower, and the pollen is then transferred from one flower to another.
Click here to see where in the world soybeans grow!