Complete Taxonomic Classification
Melanoplus
differentialis
·
Domain:
Eukarya-
Cells of
M. differentialis house
genetic material in a true nucleus. Cells also contain membrane bound
organelles.
·
Kingdom:
Animalia-
M.
differentialis
is a heterotrophic, multicellular eukaryote.
·
Phylum:
Arthropoda-
M.
differentialis
is a segmented ecdysozoan. Its body is comprised of a tough exoskeleton
with jointed appendages.
·
Class:
Insecta-
M.
differentialis
exhibits the three-part body structure (head, thorax, abdomen), three
pairs of jointed legs, two antennae, and a chitinous exoskeleton.
·
Order:
Orthoptera-
Like all
members of Orthoptera M.
differentialis undergoes an incomplete metamorphosis and has a
tympanum (ear) sensitive to vibrations for a means of communication.
·
Family:
Acrididae-
M.
differentialis
exhibits its tympanum on the side of its first abdominal segment.
Additionally, it has short antennae, which is a defining characteristic
of all the locusts (swarming grasshoppers) that occupy this family.
·
Genus:
Melanoplus-
Melanoplus
are a grass-eating and often migratory genus of grasshoppers.
·
Species:
Melanoplus differentialis-
M.
differentialis
is usually between 30 and 50mm long with females usually larger than
males. Their bodies are usually green-brown and grow darker with age.
Phylogenetic Trees
A Closer Look At Evolutionary Relationships!
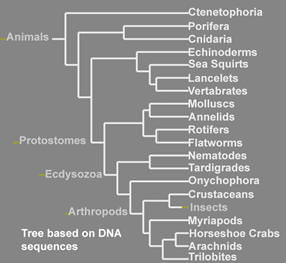
This phylogenetic tree of the animal kingdom shows that insects’ closest arthropod relatives are the Crustaceans, like lobster and crab.
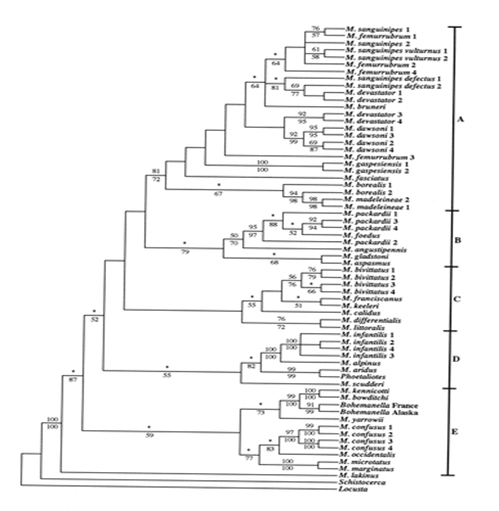
This phylogenetic tree was developed as a
phylogenetic analysis of the genus Melanoplus and was derived from
molecular data. The analysis was based on mitochondrial genes, taxa, and
specimens. Specifically, portions of four mitochondrial genes were
analyzed including: cytochrome b, cytochrome oxidase (subunits I and
II), and NADH dehydrogenase subunit II.