Classification
Domain:Eukarya
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Aves
Order: Struthioniformes
Family: Struthionidae
Genus: Struthio
Species: Struthio camelus
Domain: Eukarya
Struthio camelus is an organism in the domain called Eukarya.
Eukarya is a large branch of organisms that came from the first
prokaryotic organisms over 1.7 billion years ago! To be in this
domain, organisms must have eukaryotic cells. The prefix “eu-“
means “true” and the suffix “karya” means nucleus. So organisms
must contain a true nucleus, as well as other membrane bound cells.
Kingdom: Animalia
The kingdom Animalia is one of four Kingdoms in the Domain Eukarya. There
are several ways in which this Kingdom is set apart from the other
three Kingdoms of Plantae, Fungi, and Protista. Members of Kingdom
Animalia are multicellular, heterotrophic organisms that aquire food
by ingestion.
Phylum: Chordata
This phylum is a broad category derived from the Kingdom Animalia. All
the members of this Phlum possess a dorsal hollow nerve chord, a
notochord, pharyngeal gill slits, and a muscular tail that extends
beyond the anus at some point during development.
Class: Aves
Class Aves has many distinct characteristics. The main one being
that members have evolved parts specializing in flight (which
include hollow, lite, strong bones and powerful muscles) but most
importantly possessing feathers.
Order: Struthioniformes
This order is synonymous with that of the Order Ratite. To be
categorized in this order, the birds must be flightless.
Specifically to the Ratites, they are lacking a keel on their
sternum. Since they do not have this key part to enable wing
muscles to fly, they are lacking the ability to fly even if they
were to develop suitable wings.
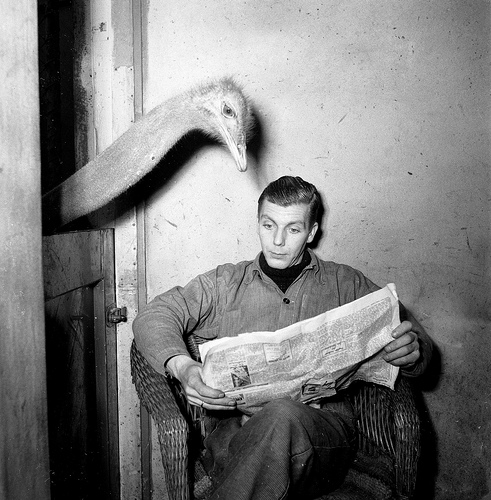
Family: Struthionidae
The ostrich has long legs and necks, and are the largest birds in
the world! They have two legs, each containing two toes.
One toe has a large claw, and the other toe is usually without
a claw.
Genus: Struthio
Even though the ostrich is a flightless bird, they still have large
feathered wings. Male and female colorings are different.
Species: Struthio camelus
There are only four living subspecies of the ostrich. All
naturally from Africa. They differ in skin tones as well as
other key factors.
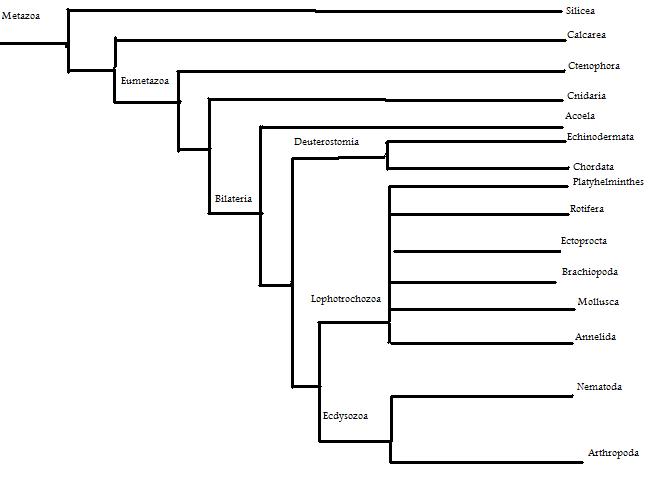
Phylogenetic trees that show how Struthio camelus relates to other organisms.
This phylogenetic tree is based on molecular data
formed by comparing ribosomal genes, Hox genes,
protein-coding genes, and mitochondrial genes (Campbell,
et al. 8th ed.) This tree shows the closest relatives of
the Phylum Chordata, which the ostrich is classified in. We
are also among this phylum, it is so interesting to see how we are
related to other organisms that one would think we have nothing in
common with.
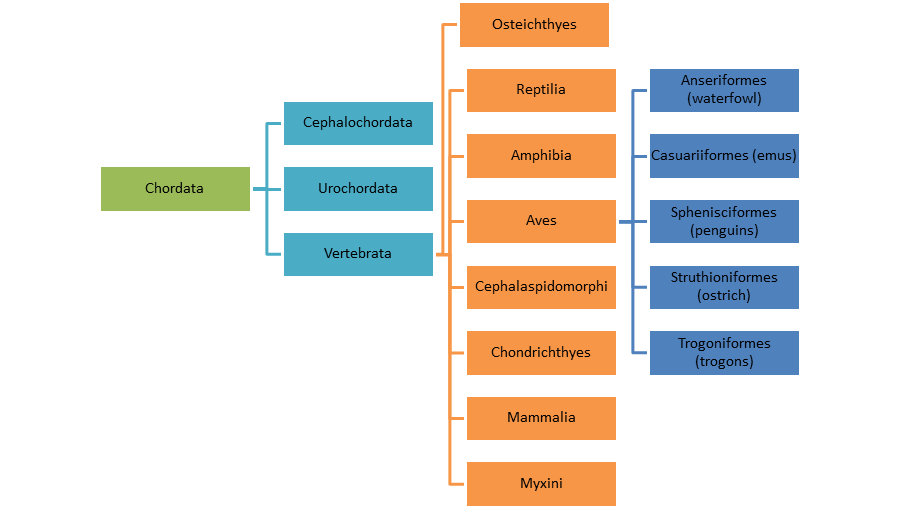
The above phylogenetic tree is based on morphological data by comparing the evolution of the different Chordates. The study of morphology is dealing with the form and structure of different organisms, and their specific structures and features The amount of species in this tree is much greater, but I have compacted the information, only showing some of the various groups of Aves. Each group has multiple species within them, making the Phylum Chordata very large. The genus Struthio starts to get specific, and leads to having only Struthio camelus. The colors of the chart are only for visual appeal, they do not have any scientific meaning behind them.
After reading about the scientific classifications about the ostrich, check out where you can find these big birds in nature by checking out their habitat!