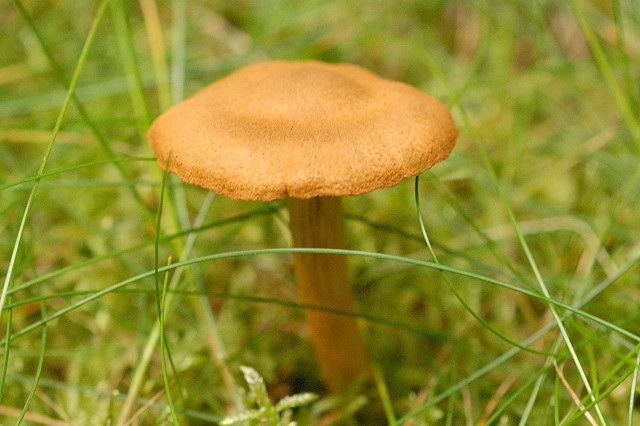
Classification
Because of the large variety of organisms, classification becomes key when it comes to a better understanding of these organisms. Below is the taxonomic classification of Cortinarius Speciosissimus
Scientific Name: Cortinarius Speciosissimus
Common Name: Deadly web caps
Domain
Cortinarius Falls under the Eukarya domain because of its possession of its membrane wrapped organelles along with possessing a true nucleolus. All organisms must posses these traits to be considered Eukaryotic.
Kingdom
The characteristic to fall under the kingdom Fungi are: Non-vascular, Chitin based cell wall, and reproduce by sporelation. Some of the most important products come from Fungi.
Phylum
Fungi are put in too different phylum's based on how they sporulate, for more info visit my reproduction page. Cortinarius s. falls In the Blasidiomycota phylum because it spawn spores off club like structures called Basida on fruiting bodies called Basdiocarps(mushrooms). They also exhibit a long dikaryon life stage. Many Plant pathogens are caused by fungi under this phylum that can effects vital crops like corn, barley, and rye
Class
The class for this fungi is Bastiomycetes, gilled mushrooms with basidocarps. Most germinate directly to form a mycelium and including the gill fungi, pore fungi, coral fungi, and bird's-nest fungi and the Giant puffball and stinkhorns.
Order
In the past centuries Agaricales have
been classified by the presence of gills used for spore bearing
structures known as Basidum. Taxanomicly speaking the order
Agaricales other wise known as “gilled mushroom” is no longer a
current group. New DNA research has proven that gills do not
necessarily indicate a relation to alike mushroom. A interesting
mushroom in this order is
Psilocybin cubensis.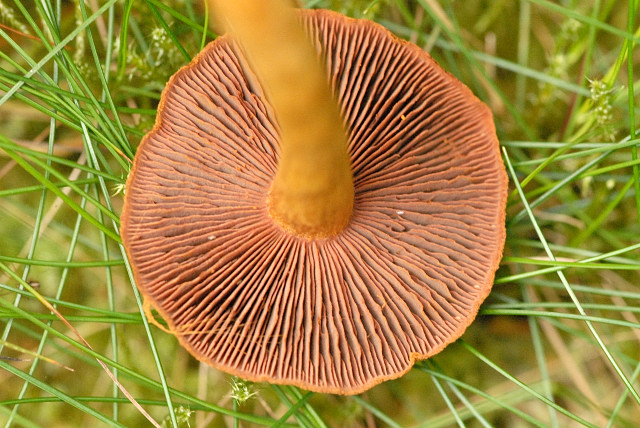 
Family
Cortinariaceae is a large family with up too 2000+ species world wide. A partial veil covers the gills in most young Cortinarius fruiting bodies. The veil joins the edge of the cap to the stem, this is composed cobweb like strands which is name the “cortina”. The deadly Toxin Orrelanine has shown to be present in large number of Cortinarius Genus. But with some being edible a large amount of identification occurs in this group. For more information how to discriminate between the lethal and safe to eat cortinarius mushroom visit my Identification page.
Genus
Mushrooms under the genus Cortinarius have mycorahazial associations with the tree in their environment. Check out my Interactions page for more info on this mutualistic relationship. The stems of the mushrooms tend to budge out in a club like fashion at the end. A key to identifications the presence of “ring zone” around the upper part of the stem, an indication of a partial veil that has deteriorated.
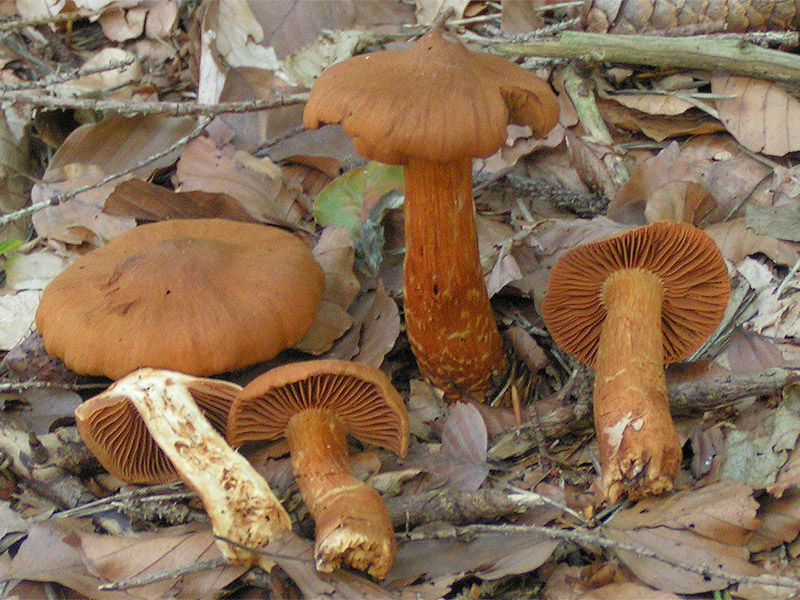

Species
Cortinarius Speciosissimus also known as Lethal web caps and has been renamed in some literature to Cortinarius rubellus. Contains Orrelanine toxin.
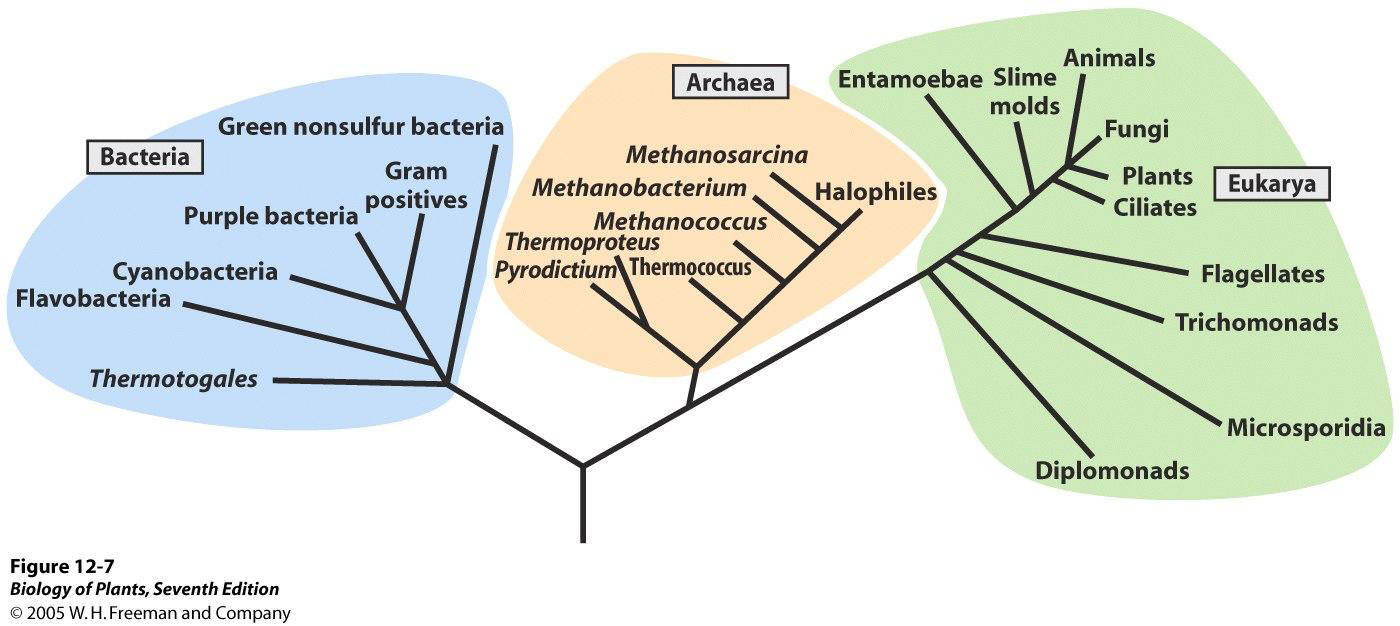
Phylogenetic Tree
What is the Tree of life?
This tree shows that all organisms evolved from a single common ancestor. From there it branched out into the three domains of life we use today. Fungi which fit in the Eukayra domain was once thought to be more closely related to plants than to animals. The organisms in the domain must have membrane wrapped organelles, and a true nucleolus. But now because of new molecular genetics technique, new data points to Fungi and Animals sharing a more recent ancestor than Fungi to plants.
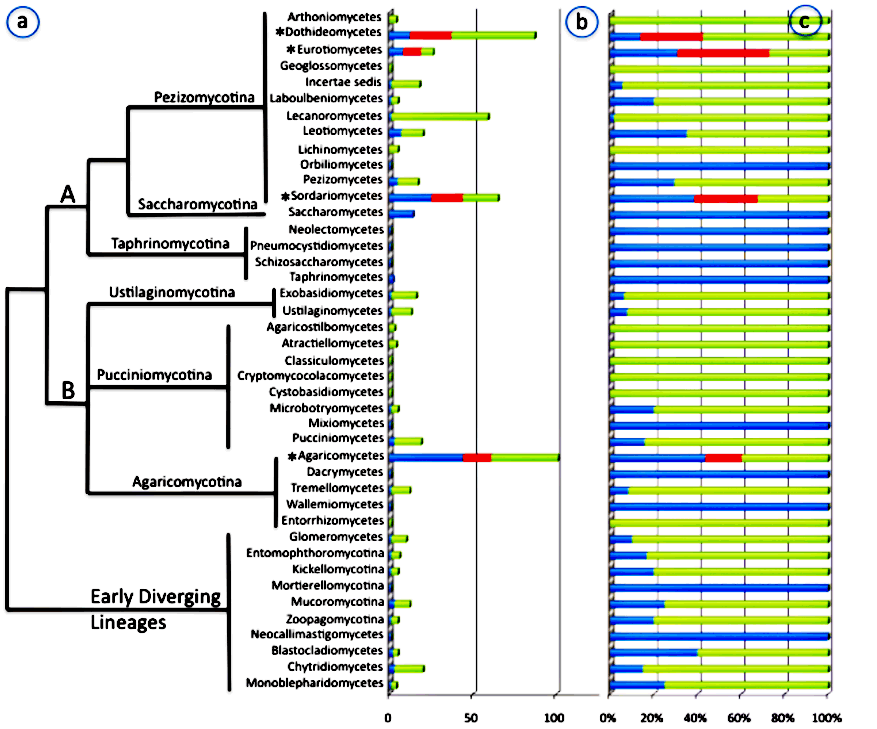
Family level sampling of fungal genomes across the Fungal Tree of Life. a) phylogenetic tree of current classification.
b) bar graphs of absolute number of families represented in genomic sampling by class or subphylum.
c) bar graphs of percentage of families represented in genomic sampling by class or subphylum.
Blue = completed or in progress, Red = proposed for Tier One sampling, Green = remaining unsampled families. A=Ascomycota, B=Basidiomycota.
*The four classes represent the most phylogenetically diverse classes of nonlichenized fungi will be Tier One targets for sequencing.
Fungal Genome Sequenced
This Phylogentic tree looks at the recent work by the, Genome Institute of the Department of Energy embarked on a five-year project to sequence 1000 fungal genomes from across the Fungal Tree of Life. Based the chart Cortinarius s. falls under the Agaricomyctes and is one of the most studied groups of all the fungi. This is most likely to the large number of mushrooms typically found in this group.