
Nutrition
Acquisition and Use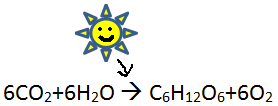
All vascular rooted plants acquire energy through a
process called photo synthesis which takes
place in the leaves. Water and carbon dioxide react with
sunlight to produce oxygen and glucose. The oxygen is usually
release into the air, so what does the plant do to replace that
empty space left when all the water and gas is gone? More water
is sucked up through the roots and xylem (non-living,
intercellular spaces) because of the pressure
changes in the leaves, much like a straw, this is because water
likes to travel from high water potential to low water potential.
After that glucose is made in
mesophyll cells (as seen above) of the leaves. It is then
transported back down to the rest
of the
 plant through different, smaller straws, called phloem
(living, inside the cells). Then
the nutrients are transferred over to the plant cells for use. In
order to keep this cycle flowing, sugars must continuously be
drained off at the sinks (branches or any growing part requiring
energy) while being replaced by new sugar from the origin (leaves or
storage root).
plant through different, smaller straws, called phloem
(living, inside the cells). Then
the nutrients are transferred over to the plant cells for use. In
order to keep this cycle flowing, sugars must continuously be
drained off at the sinks (branches or any growing part requiring
energy) while being replaced by new sugar from the origin (leaves or
storage root).
Preservation of Energy
Autumn Crocus sends up its first leaves after all the snow is gone
and the weather is warming up, using the nutrients in the ground
that were being saved all winter, it then dies off in early summer,
saving up energy and nutrients to grow its flower in the fall
instead of burning energy through the summer as well. If this flower
doesn't have leaves to photosynthesize with when it grows its
flowers where does it get the strength to do anything? When the
flower grows its leaves in the spring it stores up enough energy to
grow the blooms later in the fall.
Endomycorrhizae 
The plant can also have help getting its nutrition through
endomycorrhizae, a symbiotic relationship with fungus. This
relationship is mutualistic meaning that both organisms benefit from
the other and neither are harmed. The fungus help by increasing the
surface area of the roots through the formation hyphae (thin,
threadlike cell). A grouping of these hyphae are called a mycelium.
While the fungi assist in supplying nutrients, the plant returns
the favor by supplying the fungi with sugars from the
photosynthesis.
To see a fungus that forms ectomycorrhizae, click
here.