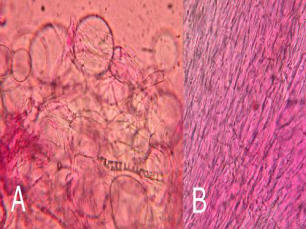
Classification
Domain
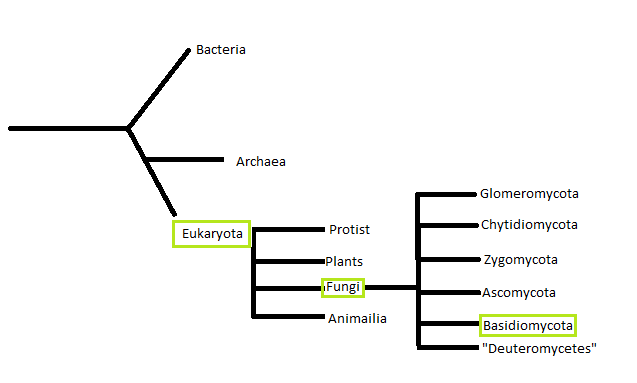
Eukarya: have eukaryotic cells, can be unicellular, colonial, or multi-cellular. Go through cell division by mitosis with a multitude of different reproduction cycles. All eukaryotes have a membrane-bound nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Includes plants, fungi, animal and protist. Some other Eukaryotic organisms include Chlamydosaurus kingii,Giraffa camelopardalis, Agalychnis callidryas
Kingdom
Fungi: Eukaryotic, have no vascular tissues for transport. Fungi reproduce with sporesPhylum
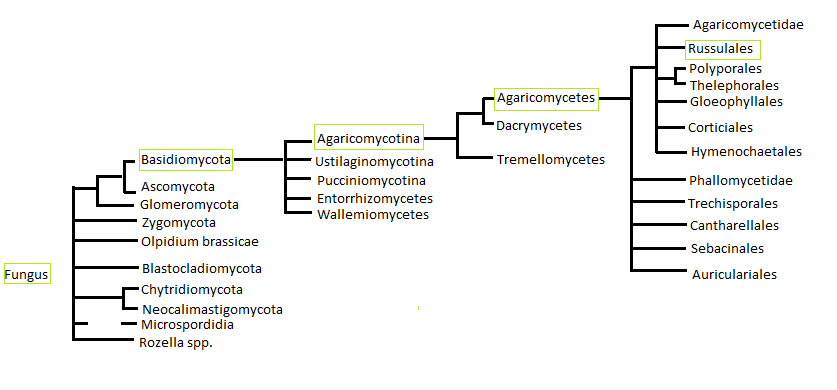
Basidiomycota: There are over 30,000 described species in the phylum Basidiomycota Spores in this phylum are borne externally on a club shaped structure called a basidium. Basdiomycota are extremely diverse they can be sexual, asexual, unicellular, or multicellular. They are so diverse that it is extremely difficult to point out unique characteristics that they all share.Class
Agaricomycetes: Contains around 16,000 different species of fungi. Agaricomycetes function as detrivores, can be parasites, can cause pathogens or be mutualistic symbionts of either plants or animals. They make a large impact through their activities at decaying wood and ectomycorrhizal mutualism of many different kinds of forest trees. Agaricomycetes are spread throughout almost all terrestrial areas but have a much smaller impact in aquatic regions.Order
Russulales: Russulales spores have elliptical or globose shapes. Most of the fruiting bodies are composed of sphaerocytes which makes them much more brittle then the average mushroom.Family
Russulaceae:1243 known species in the Russulaceae family. The fruiting bodies of these fungi break with a snapping noise and are extremely brittle.Genus
Russula: There are hundreds of Russula species that look very similar to one another, which can make it very difficult to accurately place what species a Russula mushroom is.Species
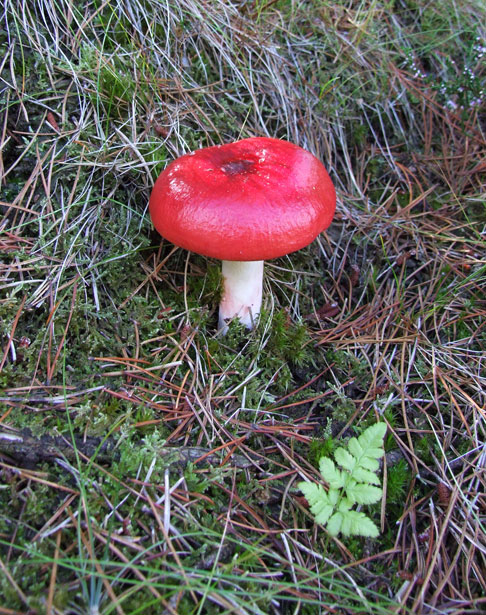
Russula emetica
Basidiomycota phylogenetic tree:
Russulales phylogenetic tree:
Identification Guide
Back to home