Reproduction
Life Cycle:
The Russula emetica follows the Basidiomycota life-cycle as it is a member of the phylum. It can undergo both asexual and sexual reproductions
Asexual:
When reproduces asexually it can either do so by asexual spores or budding. With budding there is a separation of the parent cell into a new cell and can take place in any cell. Asexual spore formation can only take place in specialized areas. These areas are called conidiophores. Dying cells divide into individual cells. Cell walls thicken to provide protection and once there are enough spores they break off and get dispersed by the wind
Sexual reproduction:
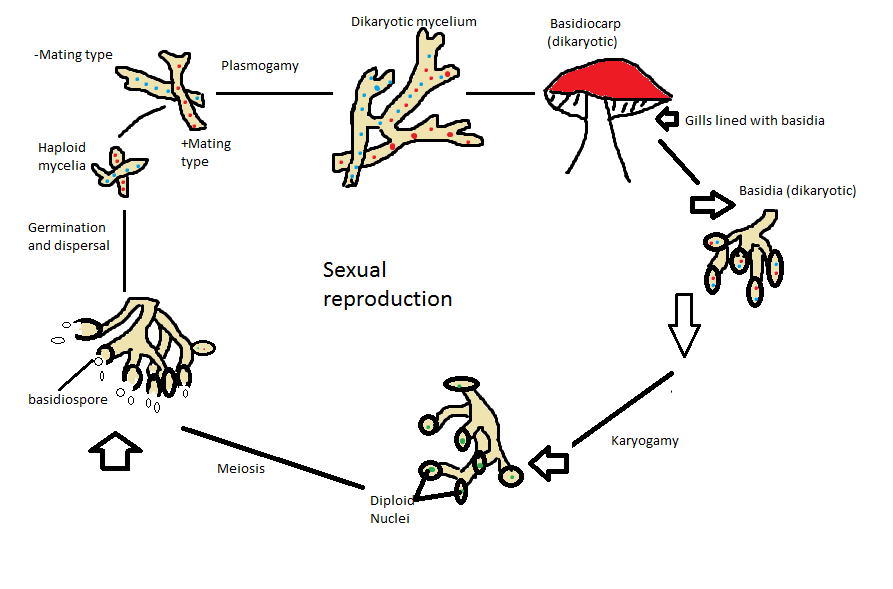
Sexual reproduction in Basidiomycota fungi happens in the fruiting body of the fungi. There are specialized structures called basidia that take over the reproductive process. From the basidia Karyogamy occurs resulting in diploid nuclei in the spores. This is then followed by meiosis, soon after which the basidiospores are released.
Spores:
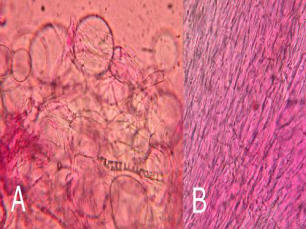 Color:
white to yellowish-white
Color:
white to yellowish-white
Shape: egg shaped or epliptical
Size: 8-10 μm
Back to home
