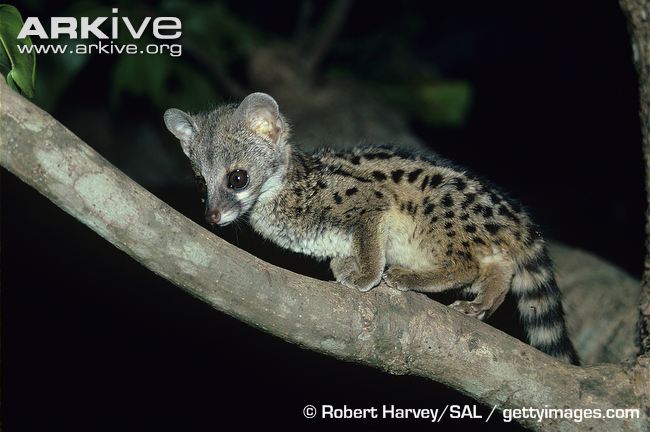
Classification
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Carnivora
Family: Viverridae
Genus: Genetta
Species: Genetta genetta
Domain: Eukarya
Eukaryotes came about from endosymbiotic event between a prontobacterium and prokaryotic cell. Domain
Eukaryote is comprised
of a vast number of organisms, all of which contain a nucleus and
other membrane bound organelles. Since the common genet is made up
of many nucleus containing, eukaryotic cells, it is classified into
Domain Eukarya.
Kingdom: Animalia
Kingdom Animalia is one of four kingdoms that are in Domain Eukarya.
To be classified as Kingdom Animalia, organisms must be
multicellular, heterotrophic, and acquire their food by ingestion.
Since the common genet is multicellular and carnivorous, it is
classified into Kingdom Animalia.
Phylum: Chordata
To be classified in Phylum Chordata, organisms must possess at some
point in their life a dorsal hollow nerve cord, a notochord,
pharyngeal gill slits, and a muscular tail. Common genets have a
spinal cord, a long tail a notochord, and gill slits in the
embryonic stage.
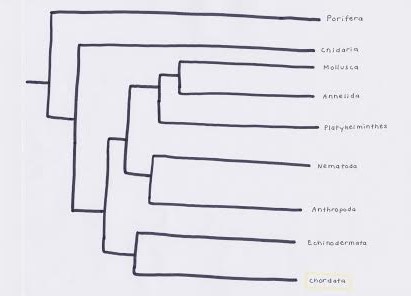
Figure 1. Phylogeny showing that the Common Genet belongs to Phylum Chordata in Kingdom Animalia. Illustrated by Jenna Sturz.
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Subphylum Vertebrata is comprised of organisms that have a skull and
a vertebral column that serves to protect the spinal cord. Common
genets have both a medium sized skull and a vertebral column.
Class: Mammalia
Class Mammalia is one of eight classes in Subphylum Vertebrata.
Organisms in Class Mammalia are endothermic, meaning they expend a
lot of energy to maintain a warm body temperature. They also have
hair, mammary glands, inner ear bones, a neocortex region of the
brain, and they care for their young. Common genets are covered in
tan and brown fur, have three inner ear bones for hearing, a
neocortex region, care for their young, and female genets have
mammary glands.
Order: Carnivora
Order Carnivora contains meat-eating mammals with slicing
carnassial teeth. Since the
common genet is a mamals and consumes the flesh of other organisms, it is classified
into Order Carnivora.
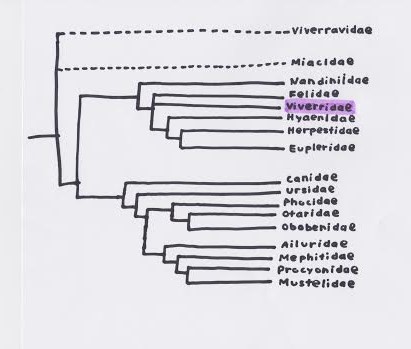
Figure 2. Phylogeny showing that the Common Genet belongs to Family Viverridae in Order Carnivora. Illustrated by Jenna Sturz.
Family: Viverridae
Organisms in Family Viverridae have four or five toes on each foot
and have half-retractable claws. They can be distinguished from
Suborder Felidae due to having five toes on their hind feet, a longer
muzzle, and shorter limbs. Although these organisms are placed in
order Carnivora, they have omnivorous diets. The common genet has a
omnivores diet, semi-retractable claws, and five toes on each feet
which classify it into Family Viverridae.
Genus: Genetta
Genus Genetta is made up of organisms that have spotted coats, long,
banded tails, small heads, and large ears. Of all the genets, the
common genet has the most variable morphologies. Genets are able to
move through any opening that their head can fit through and have
strong musk glands located by their anus. They are also highly agile
with quick reflexes and have exceptional climbing skills.
Species: Genetta genetta
Species Genetta genetta, known as the common
genet, small-spotted genet, or European genet, is the most
far-ranging species of the fourteen types of genets. The name genet
is of African origin and means “eden”.
Taxonomy
Taxonomy of Genus Genetta is under debate, so there is no Genetta phylogeny that is widely accepted. Many sympatric relationships have been found, but not enough information is known for a concise phylogeny to be developed to include the vast number of Genetta species.
Close relatives of the common genet, which are also species of
Genus Genetta, include:
Genetta abyssincia (Abysian Genet)
Genetta angolensis (Miombo Genet)
Genetta bouroni (Boborton’s Genet)
Genetta cristata (Crested Genet)
Genetta feline (S. African Genet)
Genetta johnstoni (Johnston’s Genet)
Genetta letabae (Rusty-Spotted Genet)
Genetta marculata (Rusty-Spotted Genet)
Genetta pardina (Pardine Genet)
Genetta piscivora (Aquatic Genet)
Genetta poensis (King Genet)
Genetta schoutedeni (Schouteden’s Genet)
Genetta servaling (Servaline Genet)
Genetta thierryi (Hausa Genet)
Genetta tigrina (Cape Genet)
Gentta victena (Giant Genet)
To learn all about the common genet's habitat, click here!
