|
Current Level |
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Previous Level |
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
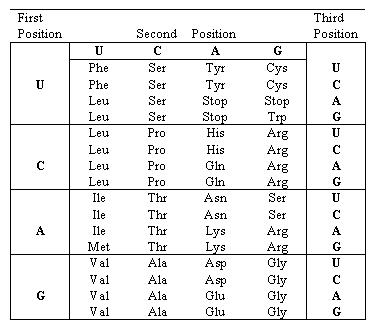
Practice problems in translation and identifying open reading frames are given below. For a review of the theory behind translations click here. You can use computer programs to check your results, but try to solve these problems by hand first, as practice for exams. |
|
|
|
1. Given the following sense strand of DNA sequence, transcribe it into mRNA, showing the orientation of the mRNA [i.e. 3' and 5' ends]. Then translate this sequence into protein [indicating amino and carboxy termini, be sure to check for an open reading frame as well.] 5' GGGATCGATGCCCCTTAAAGAGTTTACATATTGCTGGAGGCGTTAACCCCGGA 3´
|
|
2. You have just sequenced a short segment of DNA. You wish to analyze this DNA sequence to determine whether it could encode a protein. 5' TCAATGTAACGCGCTACCCGGAGCTCTGGGCCCAAATTTCATCCACT 3'
1. Find the longest open reading frame (ORF). Remember, there are six possibilities. 2. Label which strand on the DNA will be the sense strand, and which will be antisense when this DNA is transcribed. 3. Transcribe this ORF into mRNA, indicating the 5' and 3' ends. 4. Translate this mRNA into amino acids, indicating the amino (N) and carboxy (C) termini.
|
|
|
|
|
|